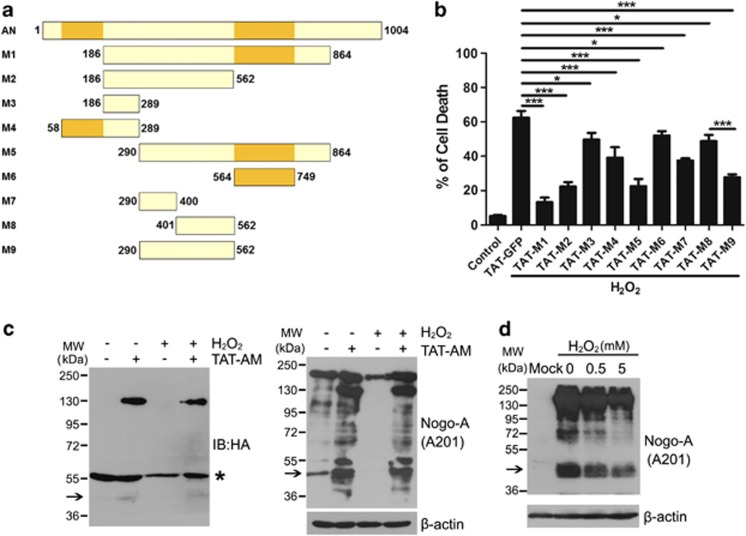
Figure 5.
In all, 290–562 residues are the pivotal domain of amino-Nogo-A for resisting to oxidative damage. (a) Schematic diagram of different deletions (M1–M9) of amino-Nogo. (b) Neurons were pretreated with 0.2 μM HIV-1 trans-activating (TAT)-M1-M9 for 2 h, followed by exposure to 50 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for another 12 h in the presence of TAT-M1-M9. Cell death rate was calculated by propidium iodide (PI) (+)/Hoechst (+). (c) Lysates from neurons treated by H2O2 with or without TAT-AM was performed to western blot with anti-HA and A201 antibodies. β-Actin was selected as a loading control. *Presented the nonspecific bands of anti-HA antibody. (d) HEK293FT transfected with mock or full-length human Nogo-A were treated with indicated concentrations of H2O2 for 1 h, and cell lysates were subjected to western blot probed with A201 antibody. β-Actin was selected as a loading control. The 48 kDa bands were pointed with arrow; n=4, mean±S.D., one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), *P<0.05; ***P<0.001