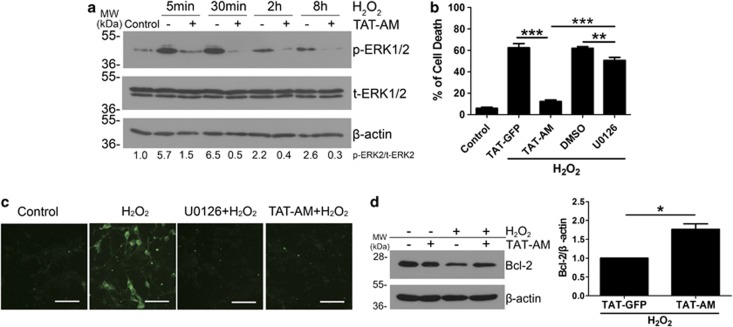
Figure 7.
Amino-Nogo-A suppresses extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) activation and Bcl-2 reduction induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). (a) Cell lysates collected from neuron cultures treated with 50 μM H2O2 for 5, 30 min, 2 and 8 h with or without pre-incubation of 0.2 μM HIV-1 trans-activating (TAT)-AM were subjected to western blot using antibody against phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) or total ERK1/2 (t-ERK1/2). β-Actin was selected as an inner standard. Quantification by densitometric scans was presented by p-ERK/t-ERK. (b) Cortical neurons were pretreated with 0.2 μM TAT-AM or 10 μM U0126 for 2 h, followed by exposure of 50 μM H2O2 for 12 h, cell death rate was calculated as before. U0126, a specific inhibitor for MEK, was used to suppress ERK phosphorylation. TAT-GFP and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) were chose as the controls for TAT-AM and U0126, respectively. (c) In all, 10 μM U0126 or 0.2 μM TAT-AM were added to neuron cultures before exposure to H2O2 for 15 min, and then cells were performed by immunofluorescence staining with anti-p-ERK antibody. (d) Lysates from neurons treated by H2O2 for 8 h with or without TAT-AM pretreatment were performed to western blot with anti-Bcl-2 antibody. β-Actin was selected as a loading control. Quantification by densitometric scans was presented by Bcl-2/β-actin. Bar=50 μm, n=4, mean±S.D., paired t-test, *P<0.05; **P<0.05; ***P<0.001