Fig. 2.
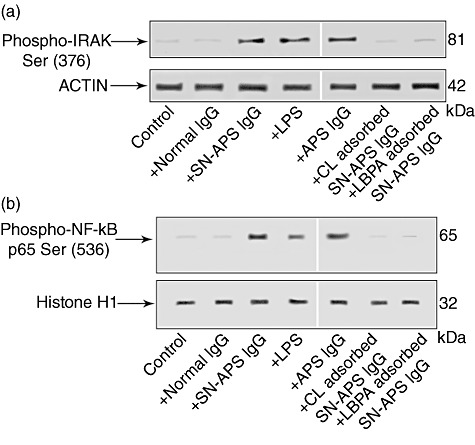
Interleukin (IL)-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) phosphorylation assay and nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation by seronegative anti-phospholipid syndrome (SN-APS) immunoglobulin (Ig)G fraction. Eahy926 cells were incubated with normal human serum IgG (NHS-IgG) (200 µg/ml), SN-APS IgG (200 µg/ml), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/ml) APS IgG (200 µg/ml), cardiolipin (CL)-adsorbed SN-APS IgG or lyso(bis)phosphatidic acid antibodies (LBPA)-adsorbed SN-APS IgG, for 45 min at 37°C, and thereafter whole and nuclear extracts were probed with polyclonal rabbit anti-phospho-IRAK or polyclonal rabbit anti-phospho-NF-κB p65, respectively. Bound antibodies were visualized with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and immunoreactivity was assessed by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL). (a) SN-APS IgG, LPS or APS IgG (200 µg/ml) induced IRAK phosphorylation; conversely, cells stimulated with control human IgG, as well as unstimulated cells (control), did not show anti-phospho-IRAK reactivity. Anti-phospho-IRAK reactivity was inhibited significantly by pre-adsorption of SN-APS IgG with CL or LBPA. As a control for loading, IRAK blots were stripped and reprobed with polyclonal anti-actin antibody. (b) SN-APS IgG, LPS (100 ng/ml) or APS IgG (200 µg/ml) induced NF-κB phosphorylation; conversely, cells stimulated with control human IgG did not show anti-phospho-NF-κB p65 reactivity. NF-κB phosphorylation was inhibited significantly by pre-adsorption of SN-IgG with CL or LBPA. As a control for loading and purity of preparation, phospho-NF-κB p65 blots were stripped and reprobed with polyclonal anti-histone H1.
