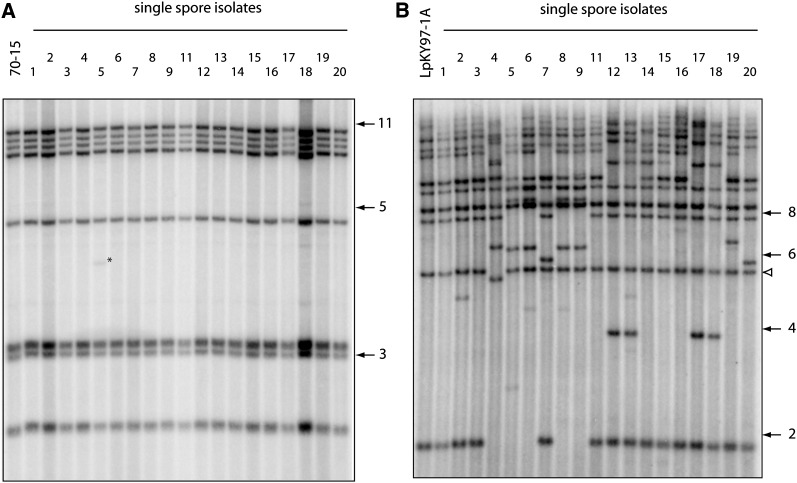
Figure 1 .
Changes in telomeric restriction fragments following two cycles of plant infection. Spores were harvested from leaf lesions, and DNA was extracted from single-spore cultures. DNAs were digested with PstI, fractionated by electrophoresis, and electroblotted to membranes. The immobilized DNAs were then hybridized with a 32P-labeled telomere probe and, finally, exposed to phosphorimage screens. (A) Telomere changes in the rice pathogen 70-15. (B) Telomere changes in LpKY97-1A. The numbers on the right of each phosphorimage represent molecular sizes in kilobases. The white arrowhead marks LpKYTEL2, a telomeric fragment that undergoes rearrangement very rarely.