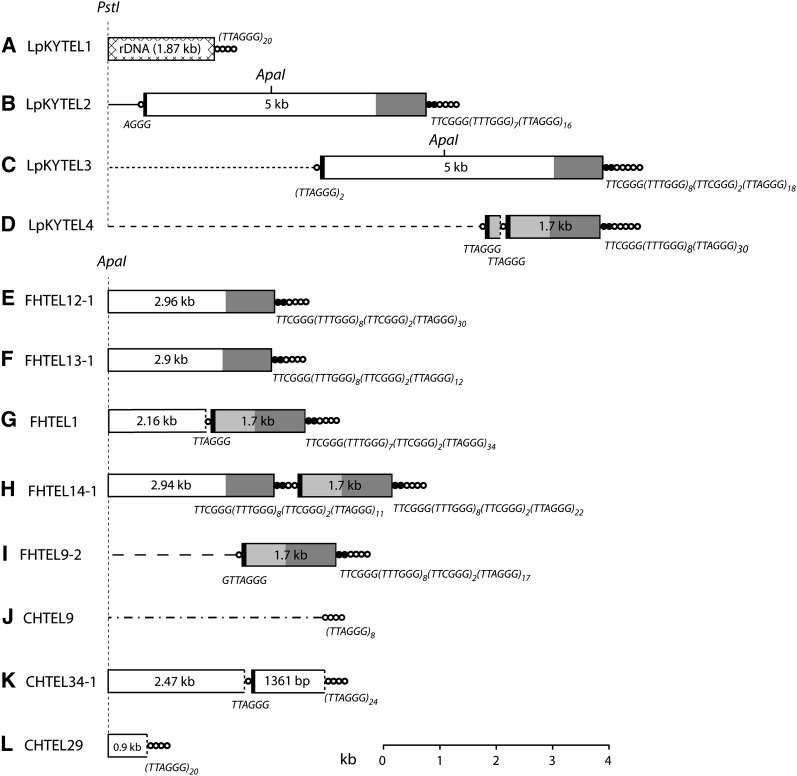
Figure 2 .
Organization of telomeric DNA in three prg-infecting strains of M. oryzae. The three strains analyzed were LpKY97-1A, FH, and CHW. Telomeres were cloned either as PstI to blunt end or ApaI to blunt end restriction fragments, and their organizations were determined by restriction mapping and sequencing. Panels A\x{2013}K show the organization of 11 cloned telomeric fragments. Telomeric sequence ([TTAGGG]n) is represented by concatenated circles and the variant telomere tract (consensus sequence: [TTTGGG]8[TTCGGG]2) is depicted by concatenated, closed circles. Repeats inserted in the telomere array are shown as boxes, and regions within the boxes having the same shading represent sequences that are identical (or nearly identical). The numbers within the boxes represent the length of each element. Truncated repeats are indicated by using dotted lines to mark the truncation boundary. Chromosome unique DNA is illustrated with a line, and the different line styles indicate that they have different sequences. The sequences of short telomere tracts (and telomere-like tracts) at the junctions of adjacent insertions are listed below the relevant junctions. Positions of PstI and ApaI restriction sites are shown. Boxes and lines are drawn to scale with the exception of the circles that represent the telomeres and telomere-like sequences.