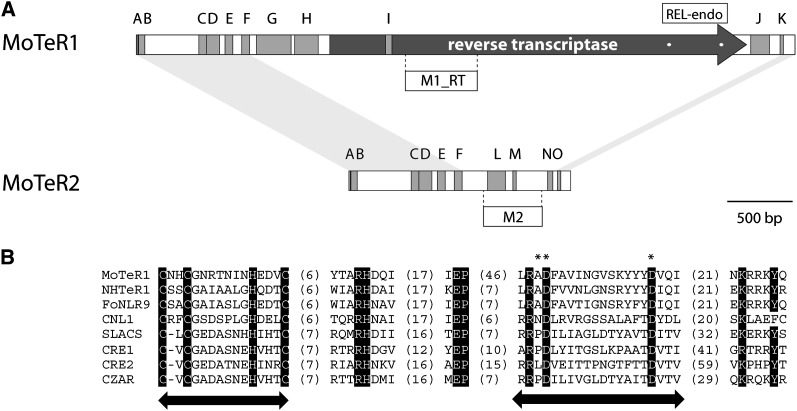
Figure 4 .
Organization of MoTER1 and MoTER2. (A) Overall structures showing positions of relevant features. Both elements are drawn to scale. Coding regions are depicted by a dark-gray arrow. Blocks of tandem repeats are shown as medium-gray boxes. The sequences and copy numbers of the individual repeat units are listed in Table S6. Light-gray shading connecting the termini of MoTER1 and MoTER2 shows regions of significant sequence identity between the two elements. The positions of the REL-endo domains and the probes used in this study are shown. (B) Alignment of the MoTeR1 REL-endo domain with those found in other retrotransposons. The names of the retroelements are listed on the left. Arrows indicate the positions of the CCHC and REL domains. Asterisks indicate the characteristic AD..D residues. Values in parentheses indicate the numbers of amino acid residues between the highly conserved motifs.