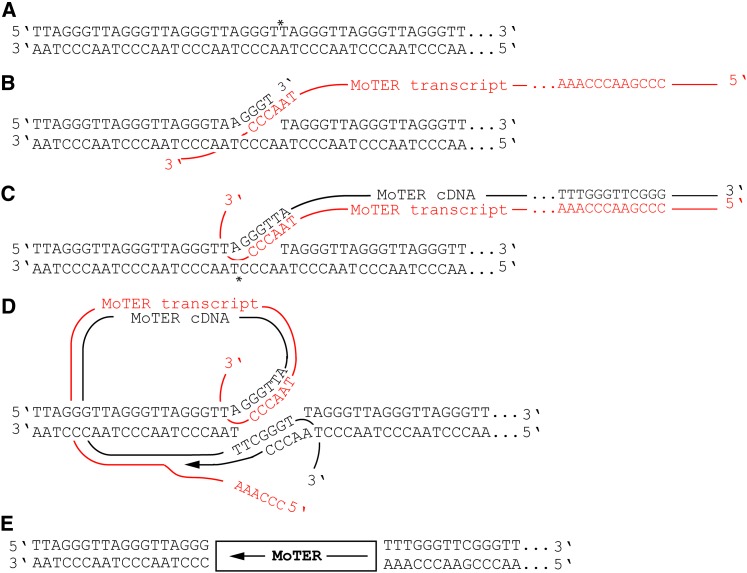
Figure 7 .
Proposed transposition mechanism for the MoTeR elements. (A) Nicking of the telomere repeat top strand by the MoTeR RT. The nick site is identified with an asterisk (note that the specific nick position is not known). (B) Annealing between the 3′ end on the top strand of the nicked telomeric DNA and the CCCTAA sequences predicted to occur at, or near, the 3′ end of a MoTeR transcript. (C) First-strand synthesis of MoTeR cDNA and nicking of the bottom telomeric DNA strand. The model shows a 3′ overhang with four nucleotides, but the length and type of overhang may be different (note that a 5′ overhang would produce a target-site deletion, as opposed to a duplication). (D) Annealing between the 3′ end released by nicking the bottom strand and the 3′ end of the newly synthesized MoTeR cDNA, followed by second-strand synthesis with concomitant RNA strand displacement. (E) Ligation of remaining nicks would result in a MoTeR element inserted precisely in the telomere repeats.