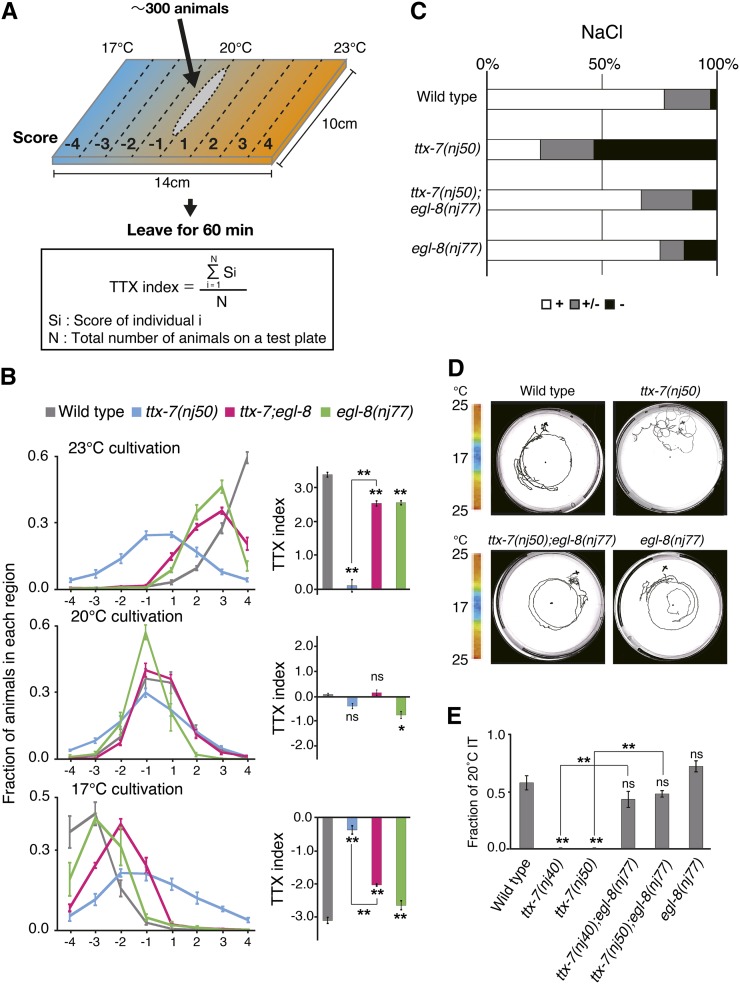
Figure 1.
Behavior of ttx-7;egl-8 double mutants. (A) Procedure for the population thermotaxis assay. Between 50 and 300 animals cultivated at a certain temperature were placed at the center of the liner temperature gradient ranging from 17° to 23° in 14 cm width. After 60 min, the number of animals at each region was counted. The TTX index was calculated using the equation shown here. (B) Distributions and TTX indices of animals cultivated at 17°, 20°, and 23°. While ttx-7(nj50) mutants showed almost athermotactic behavior, ttx-7(nj50);egl-8(nj77) double mutants migrated toward the cultivation temperatures. Tukey–Kramer test was applied (n ≥ 4 assays). The marks on the bars of each genotype represent comparisons with wild type. The marks on the lines represent comparisons between indicated genotypes. (C) Individual chemotaxis assay to NaCl. (+) strong attraction; (+/−) modest attraction; (−) no attraction to NaCl. egl-8(nj77) strongly suppressed the chemotaxis defect of ttx-7(nj50) mutants. n ≥ 57 animals. (D) Individual thermotaxis assay of animals cultivated at 20°. The center and edge of the 9-cm plate are maintained at 17° and 25°, respectively. In contrast to the random movement of ttx-7(nj50) mutants, ttx-7(nj50);egl-8(nj77) mutants showed clear isothermal tracking (IT) around 20° as well as wild-type animals. (E) Fraction of animals that moved isothermally around 20° in the individual thermotaxis assay. nj40 and nj50 are hypomorphic and putative null alleles for ttx-7, respectively. egl-8(nj77) strongly suppressed the defect of ttx-7 mutants. About 20 animals were examined in more than three trials, which were compared in ANOVA. The marks on the bars of each genotype indicate comparisons with wild type. The marks on the lines represent comparisons between indicated genotypes.