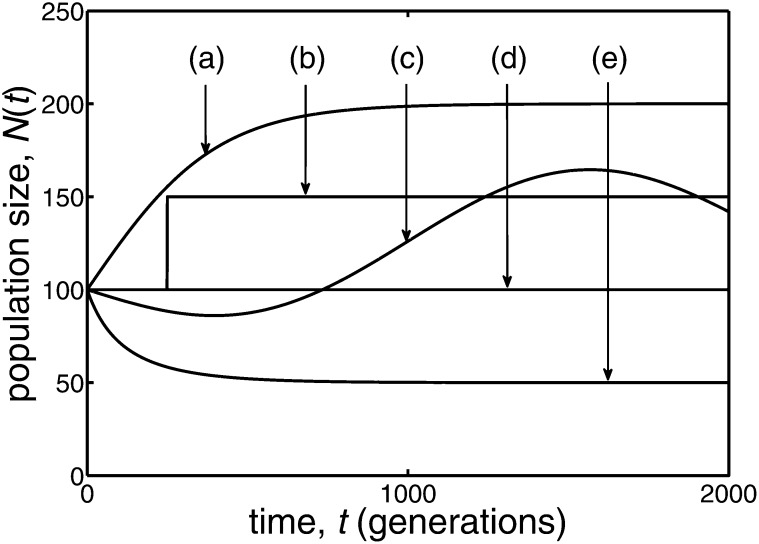
Figure D1 .
Five quite different examples of population size behavior, N(t), are illustrated. In all cases the initial population size was 100. Case a corresponds to logistic growth, with an intrinsic growth rate of 1/200 and the population size eventually doubling to 200. In case b the population discontinuously jumps to 150 individuals at generation 250, while case c has a variable population size that was derived from the sum of a constant and several different sine functions. In case d the population size remains constant, while in case e the population undergoes logistic decay, with an intrinsic decay rate of 1/200 and the population size eventually halving to 50.