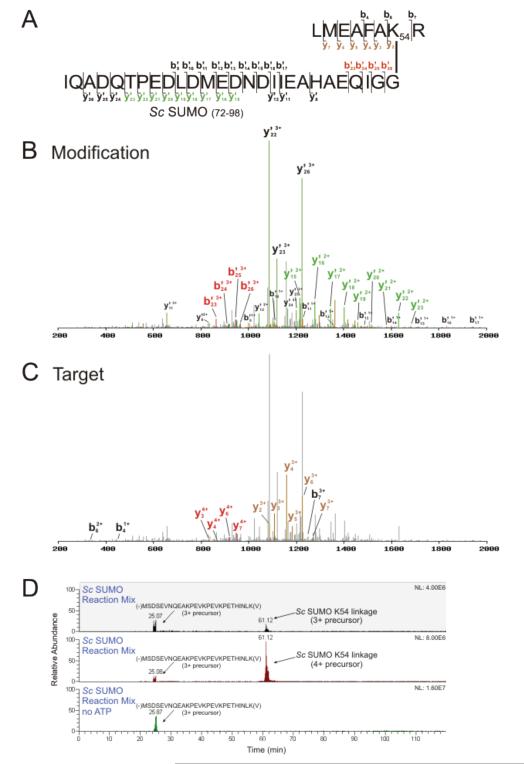
Figure 3.
A yeast SUMO K54-linkage is identified using SUMmOn. (A) Amino acid sequence of the K54-linked SUMO peptide, and the fragments assigned by SUMmOn. (B) SUMmOn-annotated CID spectrum of a yeast SUMO conjugate highlighting b’- and y’-ions derived from the C-terminal SUMO tryptic peptide, aa 72-98. (C) the same spectrum, highlighting the b- and y-ions derived from the target peptide (yeast SUMO aa 48-55). (D) EIC of representative in vitro yeast SUMO conjugation reactions with and without ATP. The m/z windows correspond to the 3+ (m/z = 1305.94-1305.96, elution at ~61 min) and 4+ (m/z=974.71-974.73) precursor ions of the SUMO K54-linked peptide. An unmodified yeast SUMO 3+ peptide MSDSEVNQEAKPEVKPEVKPETHINLK(V) (m/z window 1026.52-1026.54, eluting at ~25 min) was detected in both reactions.