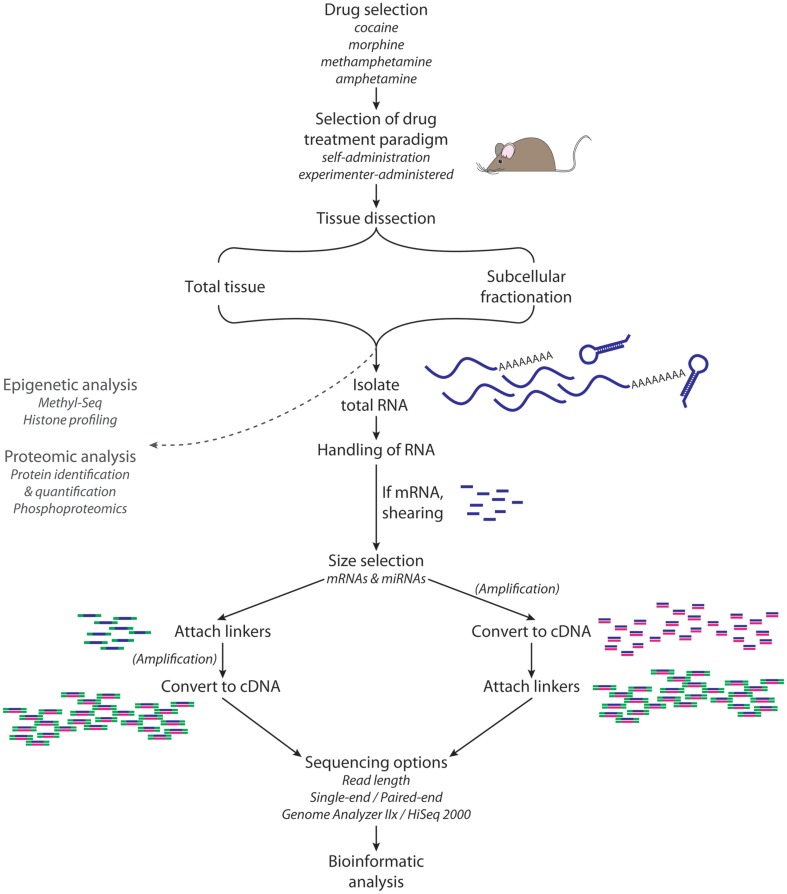
Figure 3.
RNA-Seq. High-throughput sequence analysis requires isolation of high quality RNA from the tissue, cell type, or subcellular organelle of interest. For the analysis of miRNAs, a size selection step yields RNA of the appropriate size (e.g., 18–35 nt); for the analysis of mRNAs, transcripts of the desired size are isolated and then sheared. A linker is attached to the 5′-end of each RNA fragment; a different linker is then attached to the 3′-end. Reverse transcription followed by PCR yields sufficient material for analysis. Adaptor sequences are computationally removed from the sequencing data, and then sequences are aligned with annotated miRNAs.