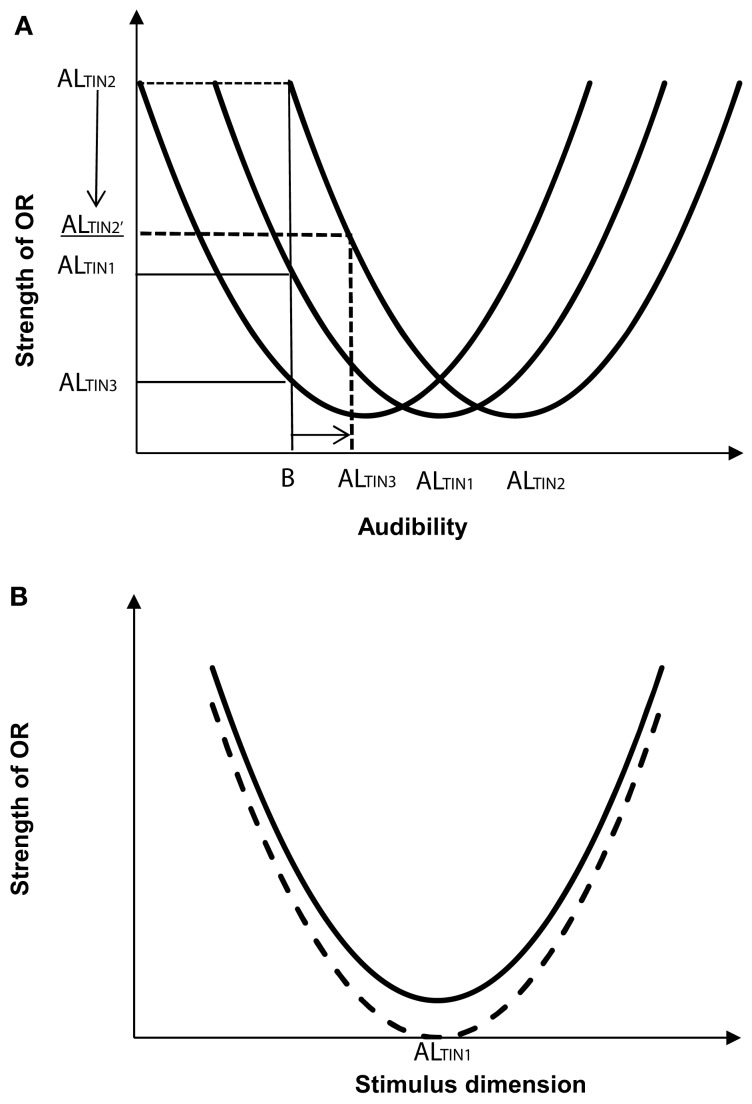
Figure 1.
(A) Theoretical relationship between orienting response (OR) to tinnitus in a background sound B as a function of different tinnitus adaptation levels (ALTIN1, ALTIN2, and ALTIN3; B < AL; based on Lauterbach, 1979, Figure 2). The curves represent signal distribution. The OR is greater to the more audible tinnitus (OR ALTIN2). An increase in background sound level (horizontal arrow) should reduce orientation to the tinnitus (illustrated for one adaptation level, OR ALTIN2 reducing to ALTIN2, the direction of change is shown by the vertical arrow). (B) OR before (top curve) and after (bottom curve) attention training. Less focus on tinnitus should reduce the strength of OR to tinnitus (shown for ALTIN2).