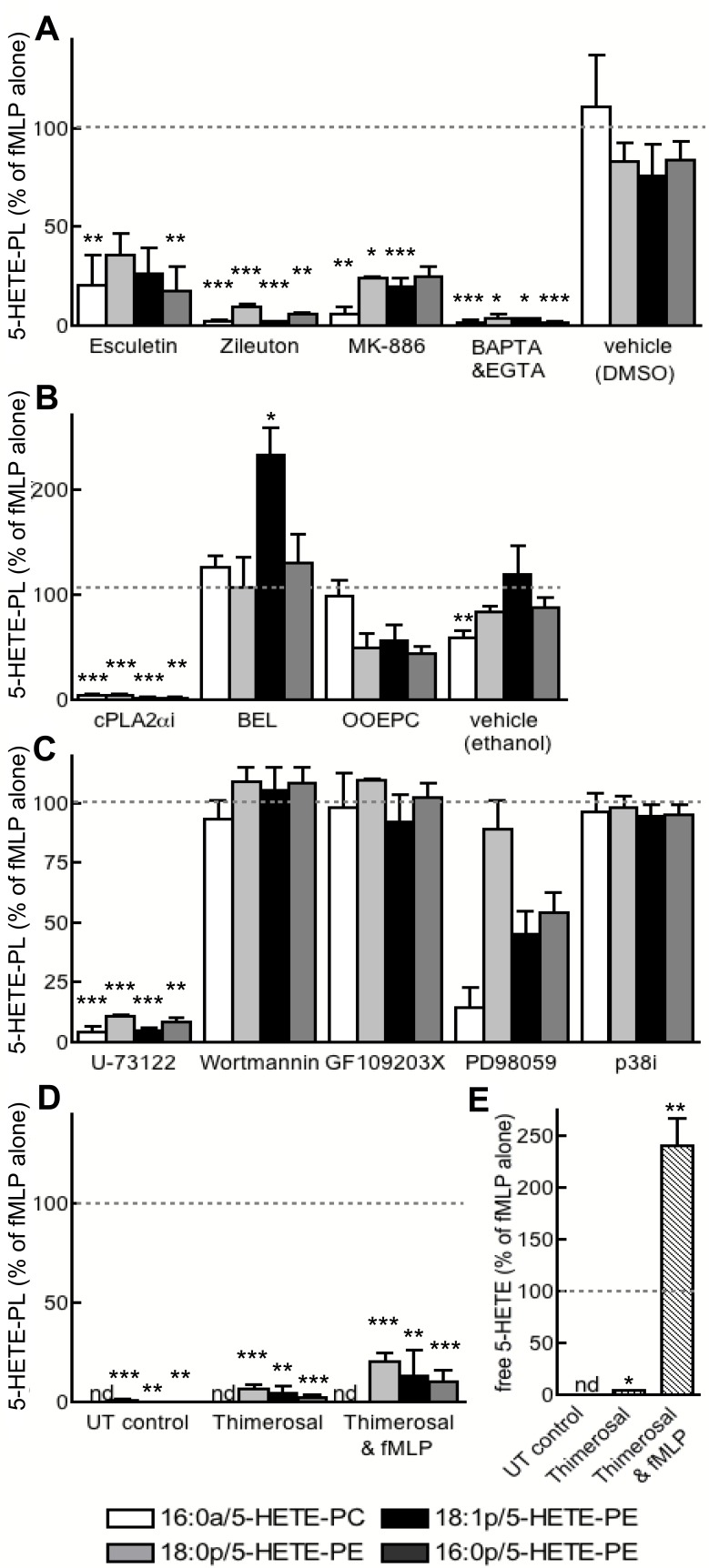
Figure 6.
Generation of 5-HETE-PLs requires 5-LOX, FLAP, Ca2+, cPLA2, and PLC and occurs by re-esterification of free 5-HETE. Neutrophils were activated with fMLP after preincubation with inhibitors as described. Lipids were extracted and analyzed with the use of LC/MS/MS. (A) Inhibition of 5-LOX (zileuton, 10μM; esculetin, 50μM), FLAP (MK-886; 1μM), cPLA2α Inhibitor (cPLAi; 10μM), or calcium chelation (BAPTA-AM, BAPTA, 10μM; and EGTA, 1mM) prevented formation of 5-HETE-PLs. (B) Inhibition of cPLA2 (cPLA2αi; 1.2μM) or secretary PLA2 (OOEPC; 10μM), but not of iPLA2 (BEL; 100nM), prevented 5-HETE-PL formation. (C) Inhibition of PLC (U-73122; 5μM) or MEK1 (PD98059; 50μM), but not p38 MAPK (p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor, P38i; 100nM) or PKC (GF109203X; 100nM) prevented 5-HETE-PL formation. (D) Inhibition of lysophospholipid acyltransferase enzymes with thimerosal (100μM) inhibited formation of 5-HETE-PLs by fMLP-activated neutrophils. (E) Thimerosal (100μM) enhanced formation of free 5-HETE by fMLP-activated neutrophils. n ≥ 3; mean ± SEM data presented from 1 experiment and representative of 3; data expressed as percentage of formation in response to fMLP alone. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001 versus fMLP alone.