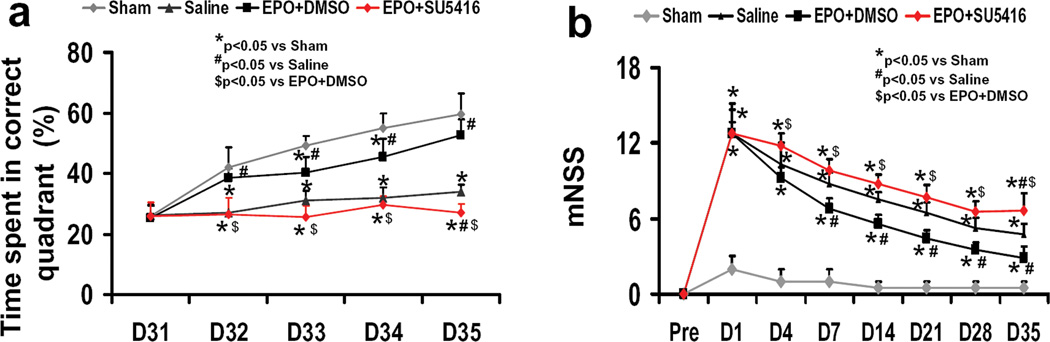
Fig. 1.
The effect of EPO and SU5416 treatment on functional outcomes. (a) Spatial learning measured by a recent version of the Morris water maze test at days 31–35 after TBI. TBI significantly impaired spatial learning at days 32–35 compared to sham controls (P<0.05). Delayed treatment with EPO improves spatial learning performance at days 32–35 compared with the saline group (P<0.05). However, the spatial learning performance at days 32–35 in the EPO+SU5416 group is worse than that in the EPO+DMSO group (P<0.05). (b) The plot shows the functional improvement detected on the modified neurological severity scores (mNSS). EPO treatment significantly lowers mNSS at days 4–35 compared to saline group (P<0.05). However, the functional recovery (mNSS) at days 4–35 in the EPO+SU5416 group is worse than that in the EPO+DMSO group (P<0.05). Data represent mean ± SD. *P<0.05 vs. Sham group. #P<0.05 vs. Saline group. $P<0.05 vs. EPO+DMSO. n (rats/group) =8.