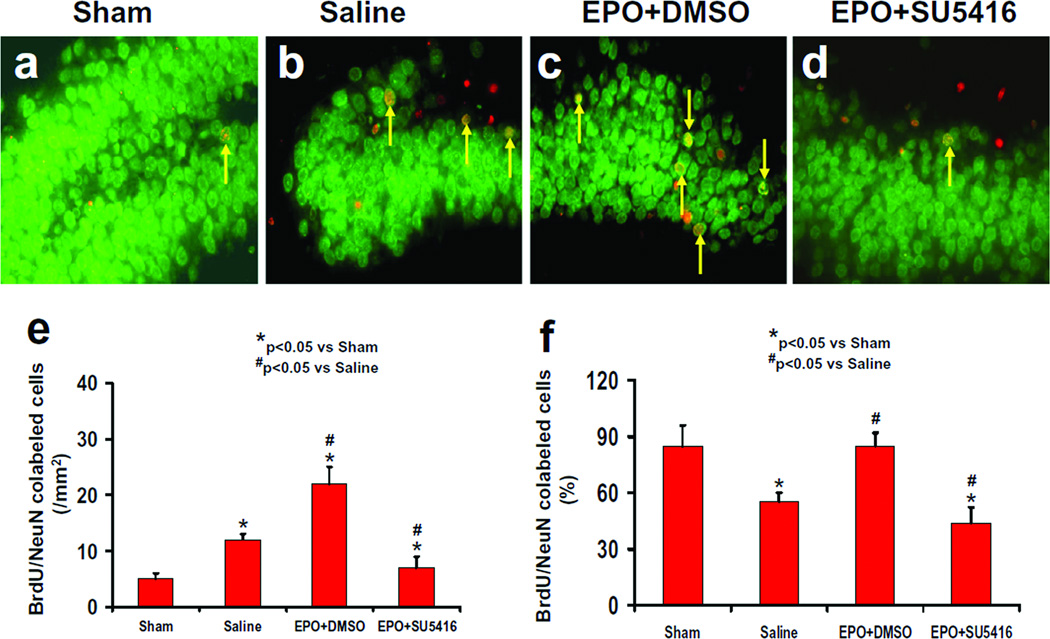
Fig.6.
Effect of EPO and SU5416 on NeuN/BrdU-positive cells in the ipsilateral DG 35 days after TBI. Double fluorescent staining for BrdU (red) and NeuN (green) to identify newborn neurons (yellow after merge, as arrows indicate) in the ipsilateral DG. TBI significantly increased the newborn neuron number in the injured DG (b) compared to sham (a; P<0.05). EPO treatment significantly increased the number of NeuN/BrdU-positive cells (c; P<0.05) compared to the saline group. As compared to the EPO+DMSO group, the EPO+SU5416 group had a significantly smaller number of NeuN/BrdU-positive cells (d; P<0.05). The bar graphs show the number (e) and the percentage (f) of newborn neurons in the DG. The number of newborn neurons (NeuN/BrdU-colocalized cells) was counted in the DG and expressed per mm2. The percentage of newborn neurons was the ratio of the number of NeuN/BrdU-positive cells to the total number of BrdU-positive cells in the DG. Data represent mean ± SD. *P<0.05 vs. Sham group. #P<0.05 vs. Saline group. n (rats/group) = 8.