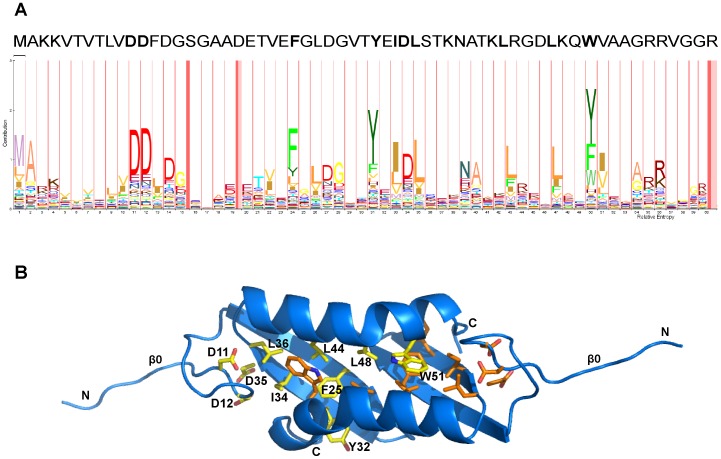
Figure 2. Conserved amino acids for the N-terminal domain of Lsr2.
(A) Relative conservation of amino acids at different positions from a multiple sequence alignment are depicted using HMM Logo (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/family/PF11774.2). The height of the letters represents the relative entropy and the width represents the relative contribution of the position to the overall protein family. The pink bars represent regions of insertion in the alignment. Amino acid residue colours reflect their biological propertes (red = charged; blues = polar, uncharged; yellows = aliphatic; greens = aromatic). The amino acid sequence for Lsr2 from M. tuberculosis is shown across the top of the HMM logo for comparison and residues that are well-conserved are in bold. (B) Cartoon diagram of Lsr2 N-terminal dimerization domain showing conserved residues. The structure is for the P21 crystal form. Conserved residues for each chain are shown in yellow and orange respectively. Yellow residues from chain A are labeled. The chain termini are also labeled.