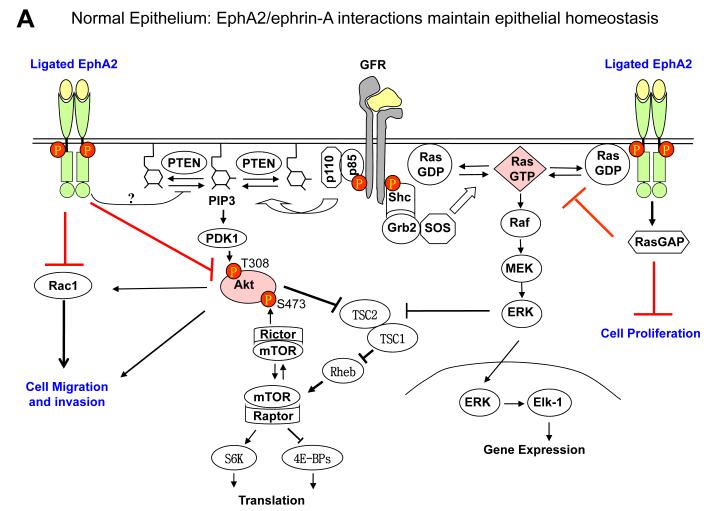
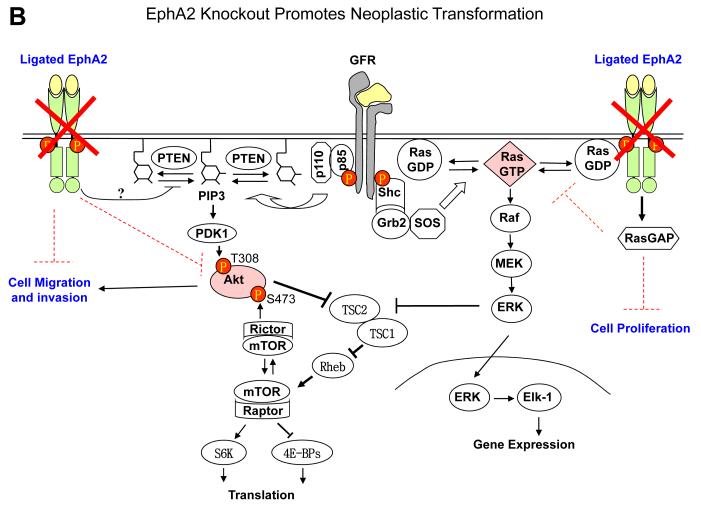
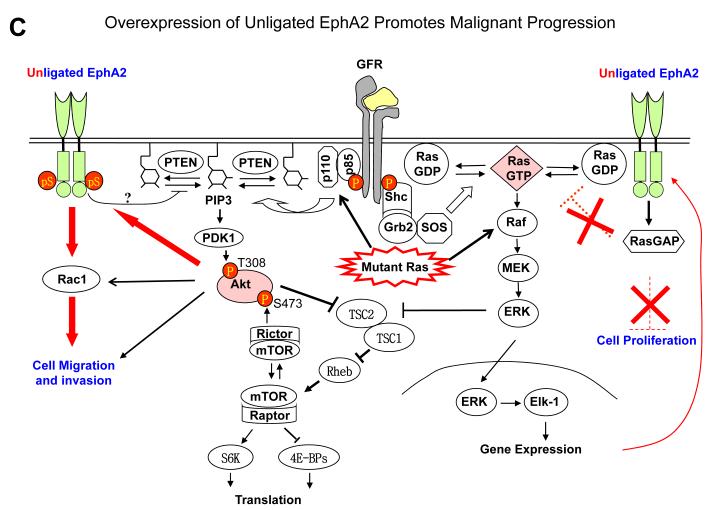
Fig. 2.
EphA2 signaling in normal epithelial cells and tumor cells. A. Under normal conditions, EphA2 and ephrin-A are properly expressed and engaged with each other. The signaling downstream from EphA2 activation by ligand engagement counteracts growth factor signaling by inhibiting activation of Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt, which contributes to the maintenance of epithelial homeostasis. B. In EphA2-null epithelial cells, the negative regulator of growth factor signaling is disrupted, which renders epithelial cells more susceptible to carcinogen insults leading to tumor development. C. With tumor progression, EphA2 can be highly upregulated whereas ephrin-A is not or downregulated, which resulting in excess of unligated EphA2. Unligated EphA2 can serve as a substrate of Akt becoming an integral component of growth factor pathway to promote tumor cell migration and invasion. At the same time, unligated EphA2 is incapable of suppressing Ras/ERK pathway.