Figure 4. LT expression on RORγt+ cells is essential for control of IL-22 production and protection of mice against C. rodentium infection.
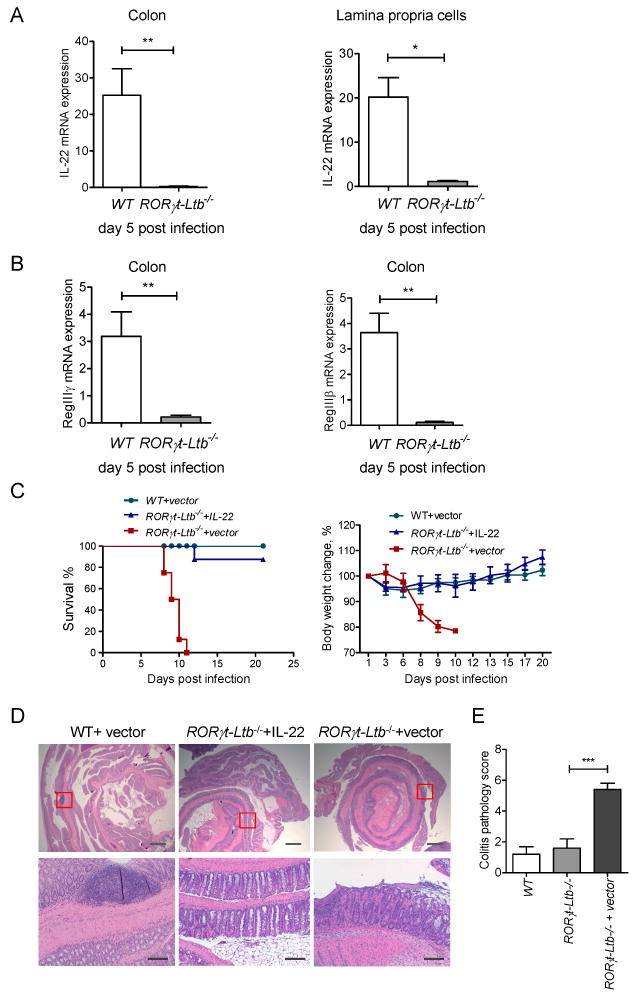
A-B. LT expression on RORγt+ cells controls IL-22 protection pathway. WT and RORγt-Ltb-/-mice were orally infected with C. rodentium. Expression of IL-22 in colon and purified lamina propria cells (A), and antimicrobial proteins RegIIIγ, and RegIIIβ (B) was measured by real-time PCR at day 5 post infection. Data represent means ± s.e.m. One out of three independent experiments with similar results is shown. n=5 mice, *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Expression data were normalized to hprt expression. C. IL-22 expression is sufficient to rescue RORγt-Ltb-/- mice from lethal C. rodentium infection. WT and RORγt-Ltb-/- mice were intravenously injected with IL-22 expressing plasmid or control vector at 6h after C. rodentium infection. n=10/group. Data combined from two experiments with similar results. Survival and body weight change are shown. D. Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of colon at day 9 post infection. Red boxes in top panel are shown at higher magnification at lower panel. Bars: 1mm for top panel, and 200μm for lower panel. E. Colitis histopathology score for mice in panel A. n=5, ***p<0.001. Data represent means ± s.e.m. One of two experiments with similar results is shown.
