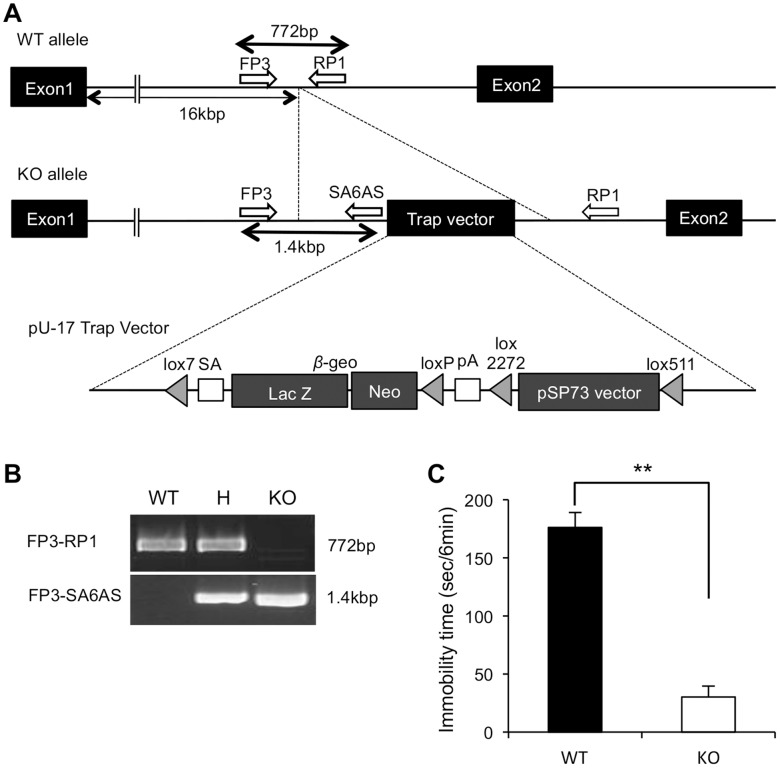
Figure 1. Generation of the Usp46 KO mice.
(A) Integration site of the pU-17 trap vector. The trap vector is inserted approximately 16 kbp downstream from exon 1. The trap vector contains a splice acceptor (SA), the β-galactosidase/neomycin-resistance fusion (β-geo) gene, a polyadeylation signal (pA) and pSP73 vector sequences [10]. The white arrows (FP3, RP1, and SA6AS) indicate the primers used for genotyping. (B) Genotyping by the polymerase chain reaction. DNA fragments of 772 bp from the wild type allele and 1.4 kbp from the inserted allele were amplified by the primer pairs FP3-RP1 and FP3-SA6AS, respectively. (C) Immobility time in wild-type (WT) and Usp46 KO mice (KO) in the tail suspension test (TST). The KO mice showed a significantly shorter immobility time than the WT mice in the TST. Data represent the mean + S.E.M. for 5–6 mice in each group. **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test).