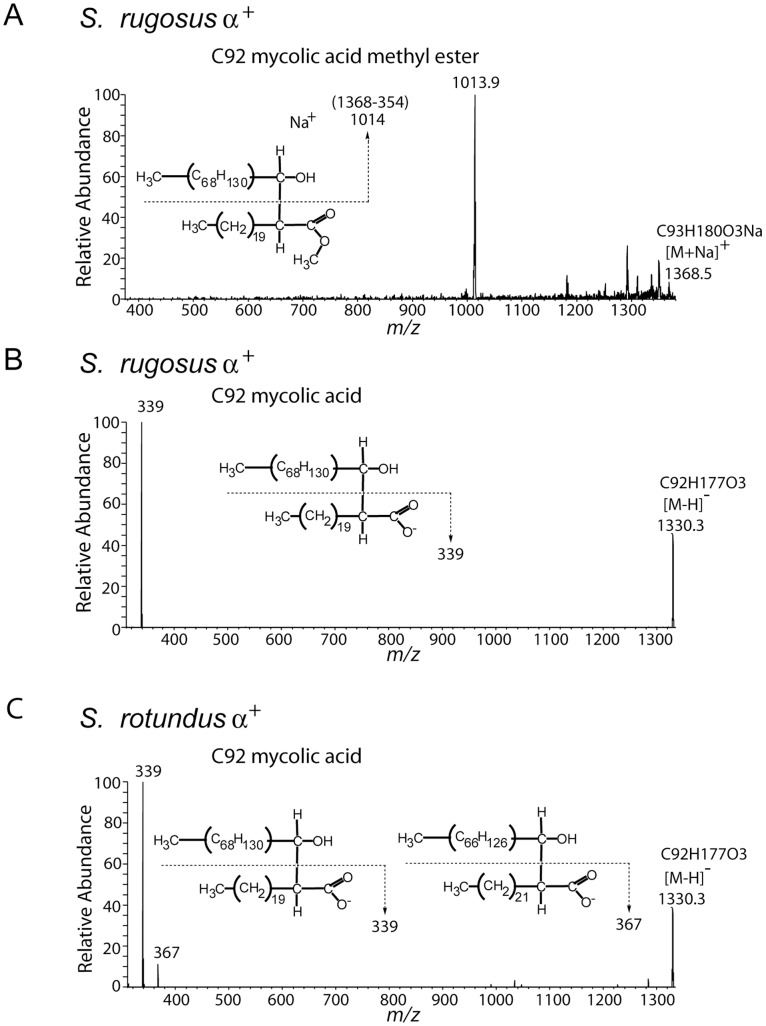
Figure 4. Collision induced dissociation mass spectrometry demonstrates alpha branch chain length.
(A) Purified S. rugosus MAMEs found in the high migrating fraction on the TLC plate were dissolved in chloroform and methanol solution, loaded into a nanospray tip and analyzed by positive-ion mode electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with ion trapping. The ion at m/z 1368.5 [M+Na]+ corresponding to C92 mycolic acid methyl ester was subjected to CID-MS, yielding a fragment ion corresponding to a sodium adduct of the meroaldehyde chain (m/z 1013.9) which indicates a neutral loss of the α-chain-derived C22∶0 methyl ester. (B–C) Bacterial pellets of S. rugosus and S. rotundus were extracted with chloroform, diluted with methanol and analyzed by negative-ion mode electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Both samples contain an ion at m/z 1330.3 ([M-H]−) corresponding to C92 mycolic acid, which was subjected to CID-MS analysis. The product ion 339 from S. rugosus (B) and ions 339 and 367 from S. rotundus (C) indicate the presence of C22∶0 and C24∶0 α-branch-derived fatty acids.