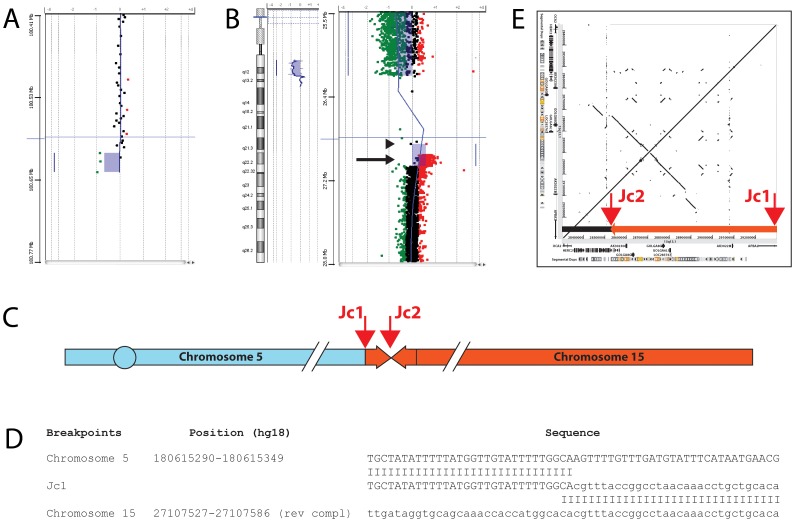
Figure 1. Molecular cloning of the 5;15 translocation in case 1.
A, magnified view of the chromosome 5 breakpoint boundary detected by array-CGH using a 244 K oligonucleotide-based whole-genome microarray. The shaded area indicates a loss in DNA copy number (deletion) detected by three oligonucleotide probes (green dots). Black dots represent probes with no changes in copy number (non-deleted region). B, whole chromosome view (left) and magnified view (right) of the chromosome 15 breakpoint boundaries detected by custom oligonucleotide-based 15q11-q13 microarray. The shaded areas indicate a deletion (majority of green dots) and a gain in DNA copy number (duplication) detected by red dots (see arrow). The area containing few widely spaced probes represents BP3, a large region containing paralogous sequences. The last deleted oligomer is at 26,210,153 bp within HERC2, corresponding to BP3; the duplicated region is between 26,996,914 (first duplicated) and 27,106,557 bp (last duplicated) with first normal oligomer at 27,108,882 bp just distal to BP3, within the APBA2 gene. An arrowhead points to the two black spots possibly indicating a single copy region between the deletion and the duplication. C, schematic representation of the rearrangement showing the two chromosomes involved, the position and orientation of the duplicated region, and the location of the two junctions (arrows). D, DNA sequences spanning the chromosome 5 deletion/15 duplication junction (Jc1) aligned with the reference sequences. E, dot-plot diagram, made with PipMaker software [45], showing the relative location of the inverted chromosome 15 duplication boundaries (Jc1 and Jc2, arrows) and of the GOLGA8E-associated inverted low copy repeat. The duplicated portion is represented by an orange arrow box.