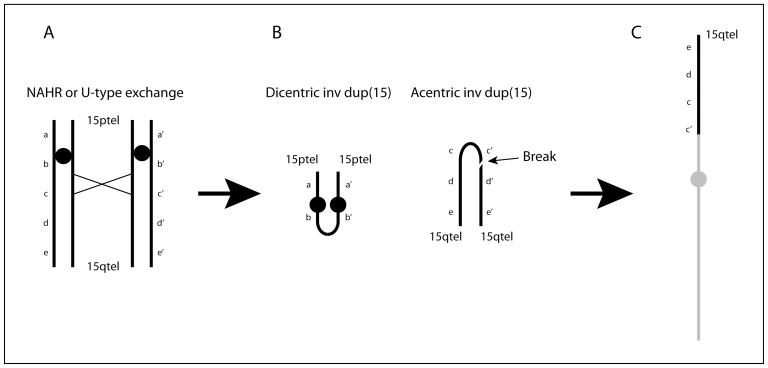
Figure 3. Schematic drawing of the putative mechanism leading to de novo unbalanced 15q translocations.
(A) at meiosis, NAHR or U-type exchange, among others between LCRs BP3: BP3 or BP4: BP5, create (B) a mirror dicentric chromosome containing the p-arm and proximal q arm and a mirror acentric chromosome containing two copies of most of the q-arm. Rearrangements mediated by BP4: BP5 will generate dicentric and acentric chromosomes containing one copy of the sequence between the repeats including the PWS/AS region (not shown). The acentric/neocentric chromosome breaks, probably randomly, in two fragments of different size and (C) one of them attaches to the distal portion of a receiving chromosome (grey line). Attachment of the larger fragment containing an inverted duplicated portion, as in our Case 1, is depicted in the drawing.