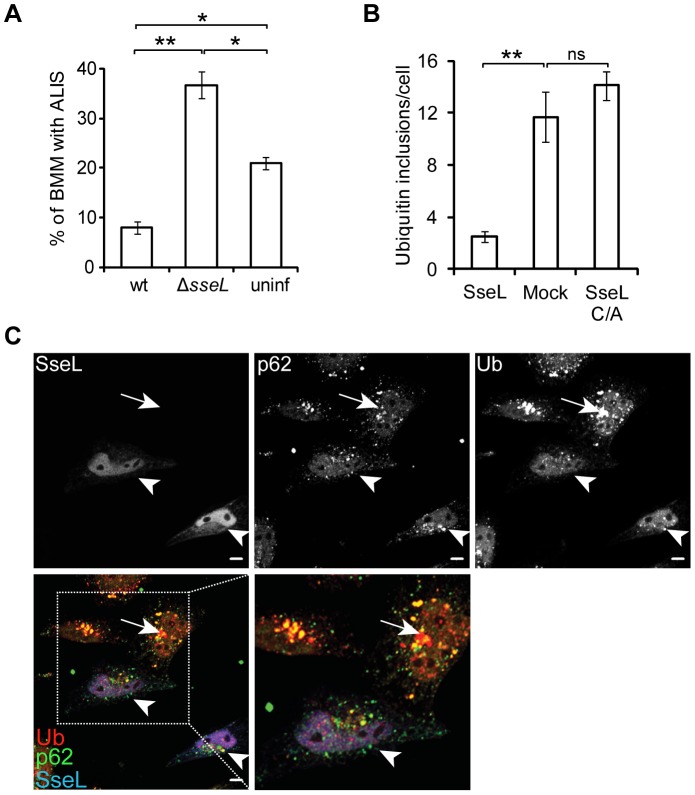
Figure 6. SseL deubiquitinates Salmonella- and puromycin-induced ALIS.
(A) Quantification of large (>2 µm), ubiquitinated aggresome-like induced structures (ALIS) in macrophages. Primary bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMM) were infected with the indicated GFP-expressing S. Typhimurium strains for 10 h, immunolabelled for ubiquitin and analysed by confocal microscopy. A minimum of 50 cells were counted for each bacterial infection per experiment and values are the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. Uninfected cells (uninf) were from the same wells as infected and therefore were exposed to extracellular bacteria. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01. (B) Quantification of the number of puromycin-induced ubiquitin inclusions in cells. HeLa cells were transfected with a vector expressing myc-SseL or myc-SseLC/A for 16 h followed by treatment with puromycin (5 µg/ml) for 4 h and immunolabelled with anti-myc, anti-p62 and anti-ubiquitin. 50 individual cells were counted per condition in each experiment. Values are the means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. ** p<0.01. (C) Single confocal sections of HeLa cells transfected with a vector expressing myc-SseL for 16 h followed by treatment with puromycin (5 µg/ml) for 4 h and immunolabelled with anti-myc (blue), anti-p62 (green) and anti-ubiquitin (Ub, red) (scale bars, 5 µm). The lower panels show a merged image of p62, ubiquitin and myc-SseL. Arrows indicate ubiquitin and p62 aggregates present in untransfected cells and arrowheads indicate cells expressing myc-SseL.