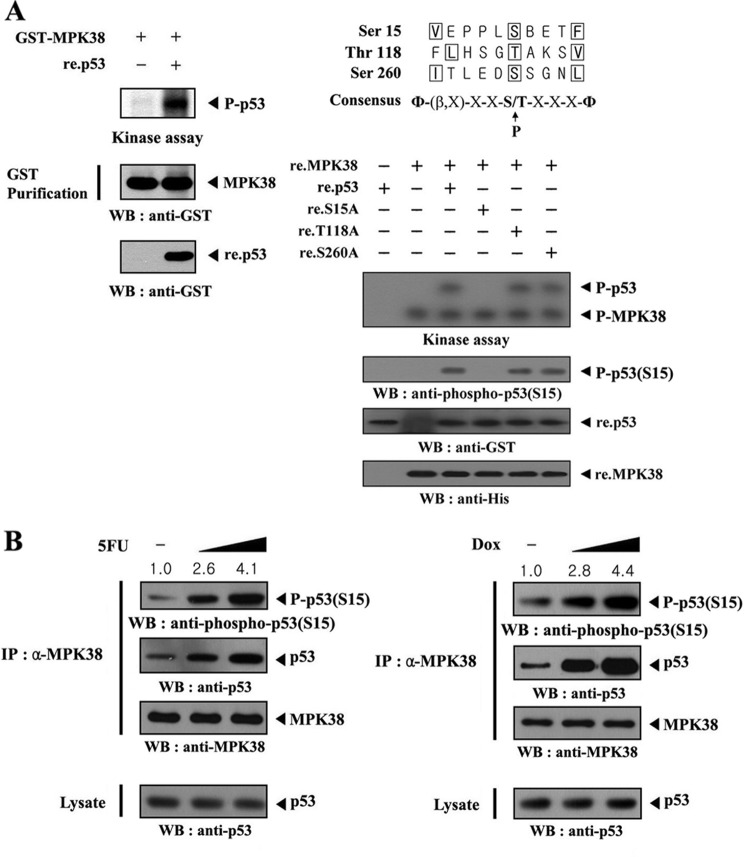
FIGURE 4.
Identification of MPK38 phosphorylation sites on p53. A, in vitro phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 by MPK38. Recombinant p53 proteins (∼3 μg) were mixed with 10 μm ATP, 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, and 10 mm MgCl2 in 20 μl of kinase buffer and incubated with precipitated MPK38 from HEK293 cell extracts containing GST-MPK38 for 15 min at 37 °C with frequent gentle mixing. Expression levels of MPK38 and p53 were monitored by immunoblotting with an anti-GST antibody (left panel). Alignment of the MPK38/AMPK consensus motif with putative MPK38 phosphorylation sites on p53 is indicated (right, upper panel). Approximately 3 μg of recombinant p53 or one of its substitution mutants (S15A, T118A, and S260A) were mixed with 10 μm ATP, 5 μCi of [γ-32P]ATP, and 10 mm MgCl2 in 20 μl of kinase buffer and incubated with recombinant wild-type MPK38 (∼4 μg) for 15 min at 37 °C (right, lower). Ser15 phosphorylation of p53 and expression of recombinant p53 and MPK38 were determined by immunoblotting with anti-phospho-p53(S15), anti-GST, and anti-His antibodies, respectively (right lower, 2nd to bottom panels). B, in vivo phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15 by MPK38. The endogenous level of p53 phosphorylation at Ser15 in the presence or absence of 5-fluorouracil (or doxorubicin (Dox)) was also analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-phospho-p53(S15) antibody. The relative level of p53 phosphorylation at Ser15 was quantitated by densitometric analysis, and the fold increase relative to untreated HEK293 cells was calculated. P-p53 and P-p53(S15) indicate the phosphorylated p53 and p53 at Ser15, respectively. Φ, hydrophobic residue; β, basic residue; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot.