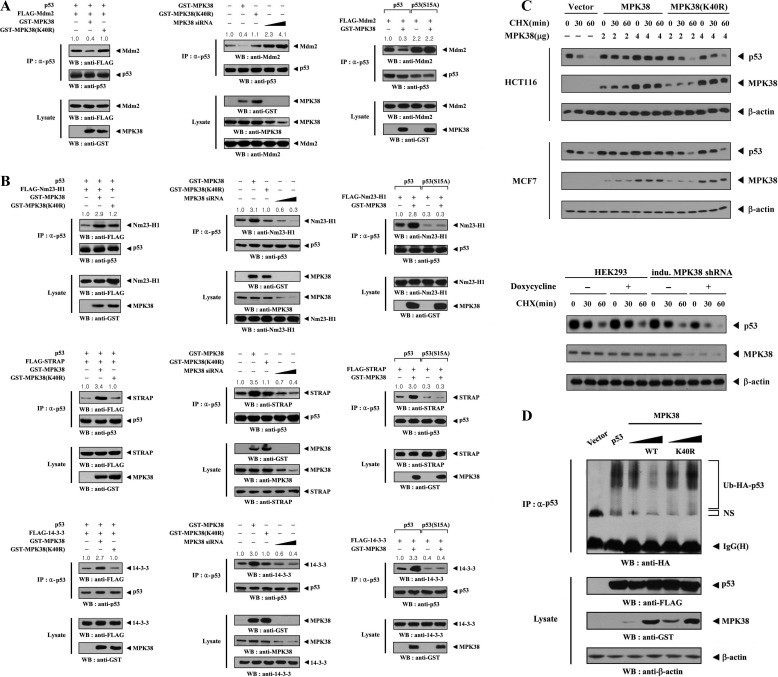
FIGURE 7.
Enhancement of p53 stability by MPK38. A and B, modulation of p53-MDM2, p53-NM23-H1, p53-STRAP, and p53–14-3-3 complexes by MPK38. HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated combinations of expression vectors for p53, p53(S15A), MDM2, NM23-H1, STRAP, 14-3-3, and wild-type or kinase-dead (K40R) MPK38, plus increasing amounts (100 and 200 nm) of Mpk38 siRNA were lysed. The lysates were then immunoprecipitated with an anti-p53 antibody (IP) and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies to determine the level of p53-MDM2 (A), p53-NM23-H1 (B, top panel), p53-STRAP (B, middle panel), and p53–14-3-3 (B, bottom panel) complexes. C, measurement of p53 stability by anti-p53 immunoblotting. HCT116 (or MCF7) cells transiently transfected with an empty vector (Vector) or increasing amounts of wild-type or kinase-dead (K40R) Mpk38, as indicated, or inducible Mpk38 shRNA HEK293 cells (indu. MPK38 shRNA) were used for immunoblot analysis. Inducible silencing of endogenous MPK38 expression by doxycycline (1 μg/ml, 72 h) was determined by immunoblotting with an anti-MPK38 antibody. Time intervals indicate the number of minutes after cycloheximide (CHX) treatment (20 μg/ml). β-Actin was used as a loading control. D, effect of MPK38 on p53 ubiquitination. p53-null HCT116 cells (23) were transfected with vectors expressing HA-tagged ubiquitin (Ub), p53, and wild-type (WT) and kinase-dead (K40R) MPK38, as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using an anti-p53 antibody (IP), followed by immunoblot analysis using an anti-HA antibody to determine the level of p53 ubiquitination. NS indicates nonspecific proteins; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot.