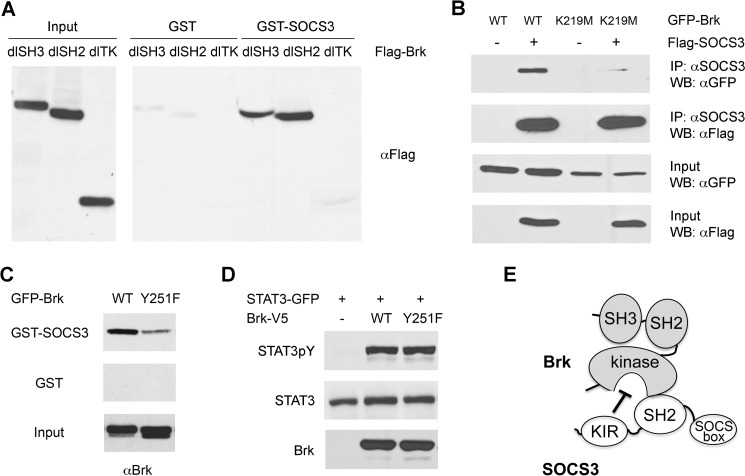
FIGURE 5.
The tyrosine kinase domain in Brk mediates interaction with SOCS3. A, binding assays of SOCS3 and Brk deletion mutants. Bacterially expressed GST or GST-SOCS3 proteins were immobilized on glutathione-agarose beads and incubated with lysates from cells expressing Flag-Brk or Flag-Brk deleted for the SH3 domain (dlSH3), the SH2 domain (dlSH3), or the tyrosine kinase domain (dlTK). Bound Brk proteins were detected by Western blot with anti-Flag antibody. Cell lysates were analyzed as input controls. B, co-immunoprecipitation between SOCS3 and Brk K219M. Cells were co-transfected with GFP-Brk wild type (WT) or Brk K219M with or without Flag-SOCS3. Cells lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-SOCS3 antibody and Western blots (WB) were performed with anti-GFP or anti-Flag antibody. An aliquot of each input was analyzed with anti-GFP or anti-Flag antibody. C, binding of wild type GFP-Brk (WT) or GFP-Brk with a site mutation Y251F was evaluated. Protein lysates from cells expressing the Brk proteins were incubated with immobilized GST or GST-SOCS3 proteins. Bound Brk was evaluated by Western blot with Brk antibodies. Brk protein input is shown in bottom panel. D, Brk Y251F kinase activity is not impaired. Lysates from cells co-expressing STAT3-GFP with WT Brk or Brk Y251F were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot with specific anti-STAT3 phosphotyrosine, anti-STAT3, or anti-Brk antibody. E, conceptual model of SOCS3 binding and inhibition of Brk.