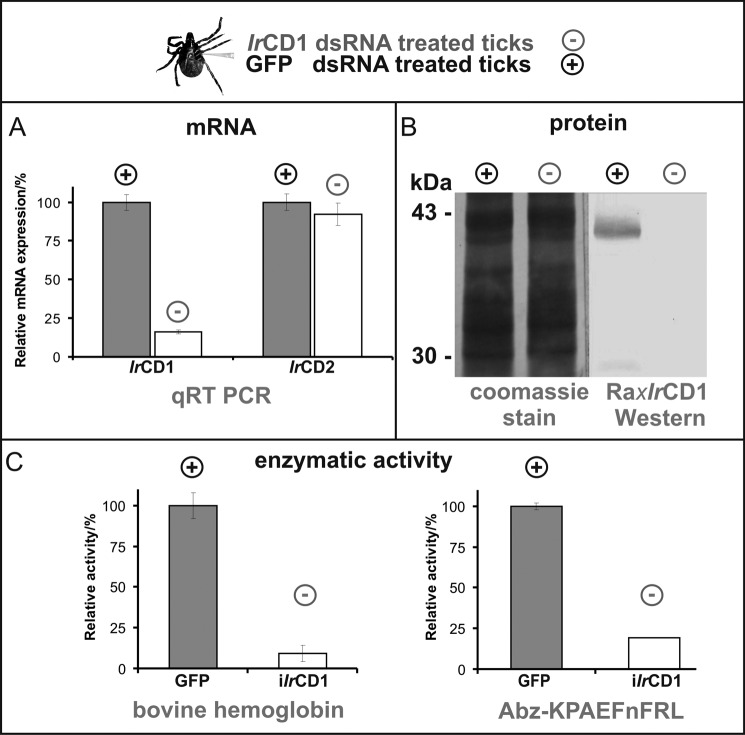
FIGURE 6.
RNAi knockdown of IrCD1. I. ricinus females (25 per each group) were injected with IrCD1 dsRNA (iIrCD1, minus, experimental group) and/or GFP dsRNA (GFP, plus, control group). Gut tissue of partially engorged ticks was used for RNA/DNA isolation and preparation of tissue homogenates. A, effect on mRNA expression levels. Dual-labeled UPL probe 78 (Roche Applied Science) and IrCD1-specific primers were used for qRT-PCR analysis of IrCD1 RNAi effect between the iIrCD1 and GFP tick groups. The presence of IrCD1 mRNA is decreased to 16% in the relative level compared with the GFP control group. For gene specificity of the IrCD1 knockdown, qRT PCR with UPL probe 44 (Roche Applied Science) and IrCD2-specific primers was performed. IrCD2 mRNA level showed no significant decrease in between the two tick groups. All PCRs were performed in triplicate. Relative values are depicted with standard deviations. B, effect on protein abundance. SDS-PAGE separated gut extracts of iIrCD1 and GFP ticks were electrotransferred to PVDF membrane (Coomassie Blue-stained lines for loading control). Presence of IrCD1 is determined by Western blot with antibody Ra×rIrCD1. No signal in iIrCD1 tick group line compared with ∼40-kDa rIrCD1 signal in GFP control group line. C, effect on gut extract cathepsin D activity. Kinetic assays measured with Abz-KPAEFnFRL and hemoglobin displayed ∼80% and >90% decrease of activity, respectively, between GFP and iIrCD1 tick groups. Measuring was performed in triplicates. Relative values are depicted with standard deviations.