FIGURE 1.
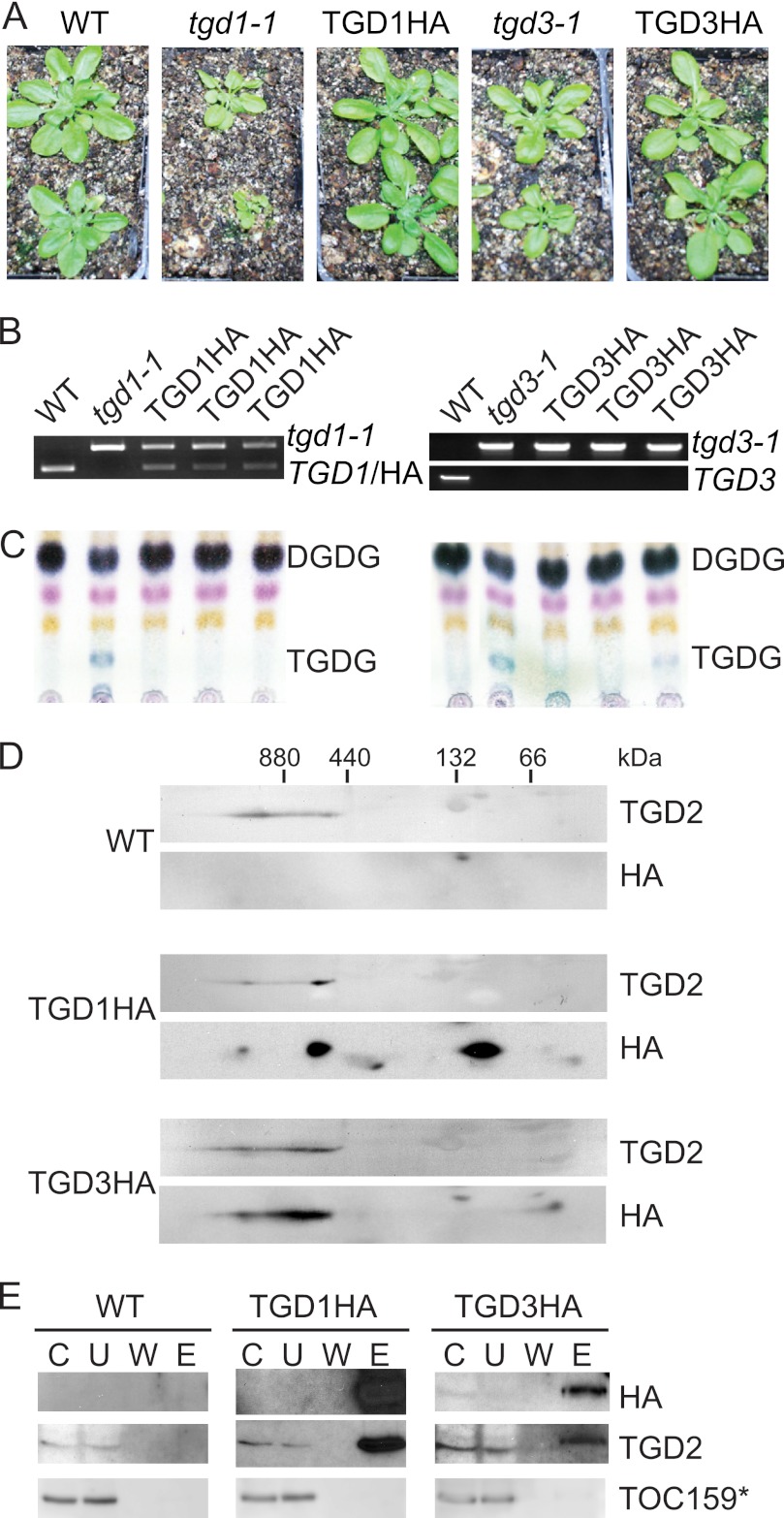
TGD1, -2, and -3 associate in a large complex. A, 28-day-old Arabidopsis are shown, with genotypes as labeled above (WT indicates wild-type Arabidopsis). TGD1HA or TGD3HA labels indicate plants homozygous for the tgd1-1 or tgd3-1 alleles, which also express TGD1HA or TGD3HA under the control of the 35S promoter, respectively. B, genotyping of plants as labeled showing the presence of the mutant tgd1-1 or tgd3-1 alleles and lack of the endogenous TGD1 or TGD3 alleles. C, α-naphthol-stained, thin layer chromatogram of lipids isolated from Arabidopsis of genotypes given at the top. Digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG) and trigalactosyldiacylglycerol (TGDG) are indicated. D, immunoblots detecting proteins indicated at the right of 20 μg of 1% dodecylmaltoside-solubilized, chlorophyll-equivalent chloroplasts isolated from Arabidopsis of genotypes indicated at the left. Protein complexes were separated in the first dimension on a 4–14% BN-PAGE (marker at top) and then denatured and run on a 12% SDS-PAGE in the second dimension. E, immunoblots detecting proteins listed at the right (TOC159* indicates the 86-kDa fragment of TOC159) of an immunoprecipitation using HA antiserum of solubilized Arabidopsis chloroplasts, genotypes given at the top. C, chloroplast starting material; U, unbound fraction; W, final wash; E, eluate.