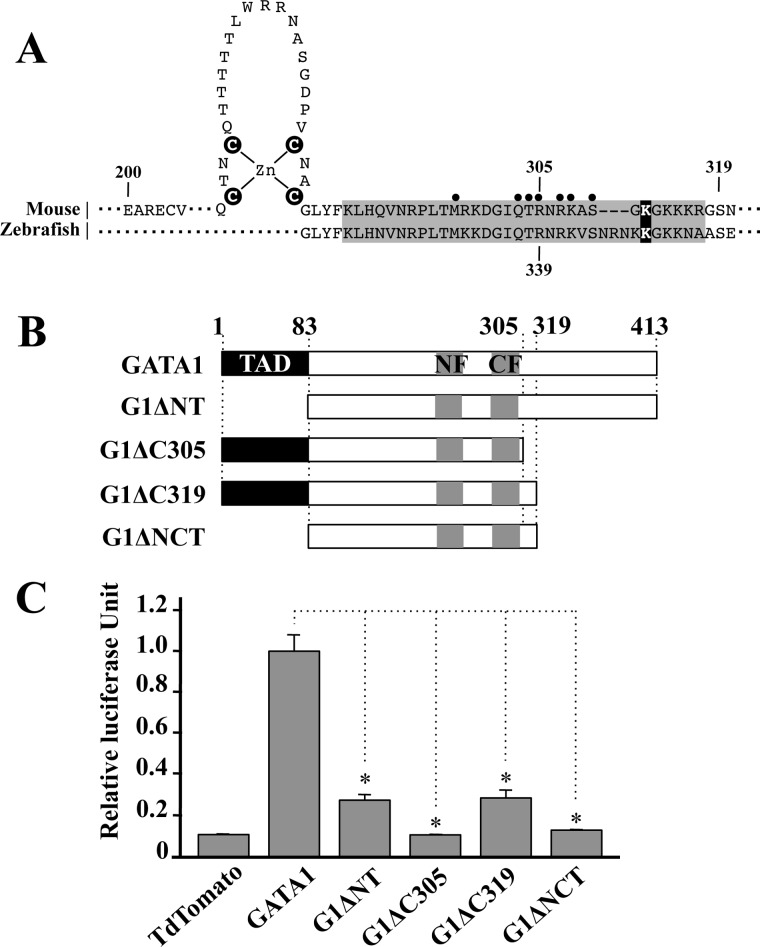
FIGURE 1.
Deletion of C-terminal region attenuates the transactivation activity of GATA1. A, sequence alignment of mouse and zebrafish GATA1 at the C-finger and basic tail regions. Basic region is highlighted with a gray background, and the closed circles indicate the amino acid residues that make direct interaction with the minor groove of DNA (28). Cysteine residues in the C-finger domain and lysine residue responsible for self-association potential are marked with a black background. B, GATA1 deletion mutants are schematically illustrated. Numbers indicate position of amino acid residues. C, transactivation activity of GATA1 mutant proteins. Note that transactivation activity is significantly reduced by the deletion of C-terminal region. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (*, p < 0.05).