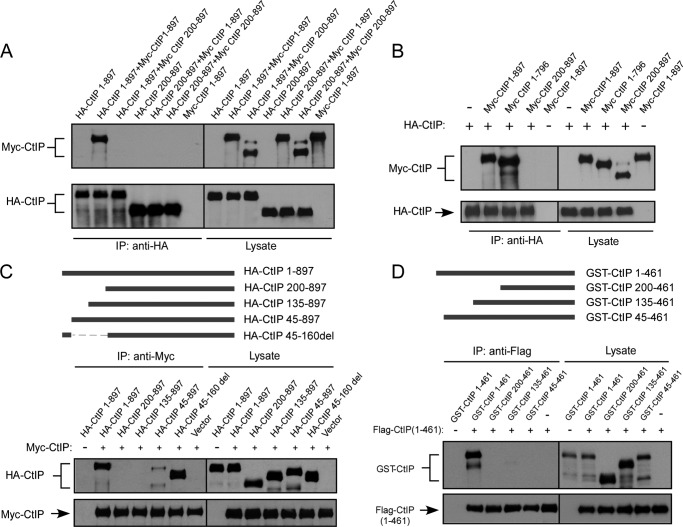
FIGURE 1.
CtIP N terminus residues 1–45 mediate dimerization of CtIP. A, 293T cells were co-transfected with HA-CtIP 1–897 (wild type) and Myc-CtIP 1–897 or Myc-CtIP 200–897 or co-transfected with HA-CtIP 200–897 and Myc-CtIP 1–897 or Myc-CtIP 200–897. Anti-HA immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed, followed by anti-Myc Western blotting. B, removal of N terminus but not C terminus prevents binding of Myc-CtIP with HA-CtIP. 293T cells were co-transfected with HA-CtIP and Myc-CtIP, Myc-CtIP 1–796, or Myc-CtIP 200–897. Anti-HA IP was performed, followed by anti-Myc Western blotting. C, the N terminus from amino acids 1–45, but not amino acids 45–160, is important for mediating dimerization of CtIP. HA-CtIP N-terminal deletion mutants were generated as indicated (top panel). 293T cells were co-transfected with Myc-CtIP 1–897 and HA-CtIP 1–897 or the indicated N terminus deletion mutants. Anti-Myc IP was performed, followed by anti-HA Western blotting. D, residues 1–45 are important for dimerization of N terminus CtIP in vitro. GST-CtIP N-terminal deletion mutants were generated as indicated (top panel). FLAG-tagged N-terminal CtIP 1–461 and GST-tagged N-terminal CtIP 1–461 or indicated deletion mutants were expressed in SF21 insect cells by baculovirus infection. Immunoprecipitation was performed using anti-FLAG M2 beads (Sigma) followed by anti-GST immunoblotting.