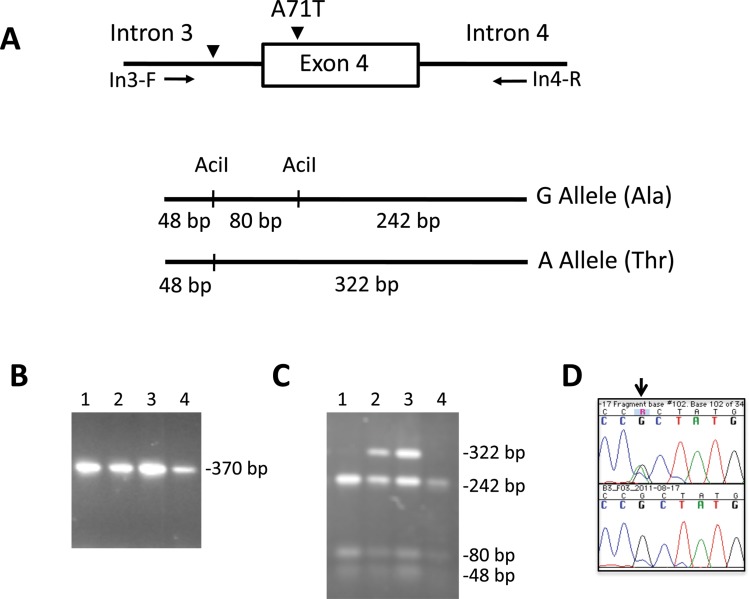
Figure 4.
Genotyping of the Ala71Thr substitution in exon 4 of BLK. (A) Schematic diagrams showing the procedure for genotyping the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs55758736 in exon 4 of BLK. Genomic DNA was amplified with primers flanking exon 4 (In3-F: 5′AGAAGCCTGTCCTCCTTGGTAGC 3′ and In4-R: 5′GGAAAGATTTTGGAGAGGAAGACA 3′) and the PCR products were digested with the restriction enzyme AciI. The A allele disrupts the restriction site generating only two fragments of 48 and 322 bp while the G allele produces three fragments of 48, 80 and 242 bp. (B) PCR products of four subjects showing a unique band of 370 bp and (C) the subsequent AciI digestion of the amplification products. Subjects 2 and 3 are heterozygotes (G/A) and subjects 1 and 4 are homozygotes for the wild type allele (G/G). (D) Sequence chromatographs showing one subject heterozygous for the BLK mutation (above) and one subject homozygous for the wild type allele (below).