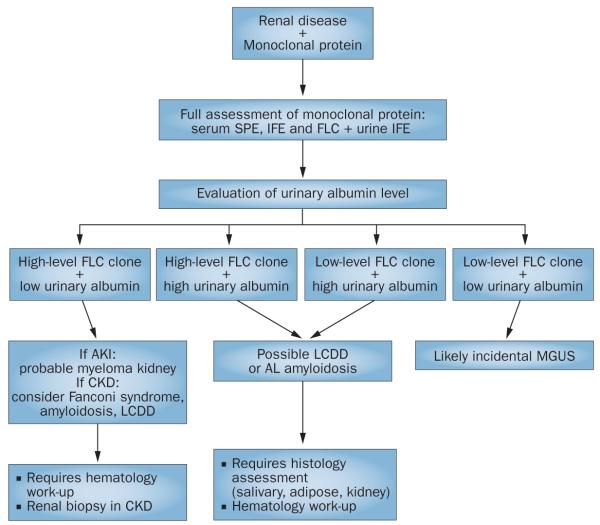
Figure 3.
Diagnostic approach to a patient with renal disease and a monoclonal protein. Combining the evaluation of urinary albumin concentration with the level of the FLC clone can guide the management of a patient with renal injury and a monoclonal protein. Tubulointerstitial pathologies are more likely when urinary albumin levels are low and FLC levels are high. By contrast, patients with AL amyloidosis and LCDD frequently have high urinary albumin levels. These pathologies are often associated with a lower level of FLC clone, but can occur with any FLC level. Where diagnostic uncertainty remains, assessment of histology is essential. Abbreviations: AKI, acute kidney injury; AL, amyloid light chain; CKD, chronic kidney disease; FLC, free light chain; IFE, immunofixation electrophoresis; LCDD, light chain deposition disease; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; SPE, serum protein electrophoresis.