Fig. 2.
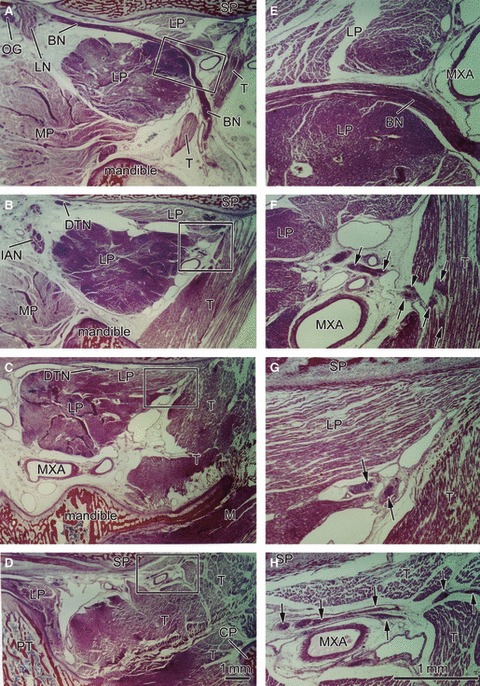
Sagittal sections of a 22-week-fetus (CRL 185 mm) showing a longitudinal course of the buccal nerve. Panel A is the most medial side of the figure, and panel D the most lateral side. The right-hand side of the figure corresponds to the anterior side of the head. Panels E–H are higher magnification views of squares in panels A–D, respectively. Intervals between panels are 4 mm (A–B), 7 mm (B–C) or 3 mm (C–D), respectively. The buccal nerve (BN) is longitudinally cut in panel A. The lower head of the lateral pterygoid muscle (LP), cut transversely, is larger than the upper head, most of which is cut longitudinally in the anterosuperior side of the nerve course. Both heads are attached in panel C. The BN also passes through the inferomedial part of the temporalis muscle (T). The anterior deep temporal nerve from the BN enters the T in panel F, whereas the other deep temporal nerves (DTN) end in panel H. These nerves are indicated by arrows in the higher magnification views (panels E–H). Dark staining in parts of the lateral pterygoid and temporalis muscles appears to be due to postmortem change different from other muscles. Panels A–D (or Panels E–H) have been prepared at the same magnification (scale bars in panels D and H). BN, buccal nerve; CP, coronoid process of the mandible; CTN, chorda tympani nerve; DTN, deep temporal nerves; IAN, inferior alveolar nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; LN, lingual nerve; LP, lateral pterygoid muscle; MC, Meckel's cartilage; MN, mandibular nerve; Mn, masseter nerve; MP, medial pterygoid muscle; MXA, maxillary artery; MXN, maxillary nerve; OG, otic ganglion; PT, cartilaginous pterygoid part of the sphenoid (independent from the other parts); PTT, pharyngotympanic tube; RC, Reichert's cartilage; SP, sphenoid bone anlagen; T, temporalis muscle; ZA, zygomatic arch.
