Fig. 6.
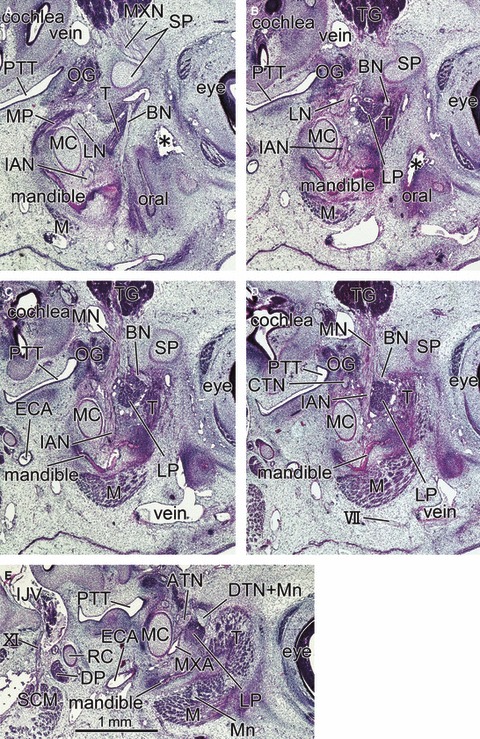
Sagittal sections of a 6-week-embryo (CRL 20.5 mm) showing the primitive lateral pterygoid muscle at a wedged position between the buccal nerve and inferior alveolar nerve. Panel A is the most medial side of the figure and panel E the most lateral side. The right-hand side of the figure corresponds to the anterior side of the head. All panels are prepared at the same magnification (scale bar in panel E). Intervals between panels are 0.3 mm (A–B), 0.15 mm (B–C), 0.2 mm (C–D) or 0.35 mm (D–E), respectively. In panel A, the buccal nerve (BN) runs inferiorly along the medial aspect of the temporalis muscle (T) toward the oral cavity (oral). In panels B–D, the nerve runs laterally along the superior margin of the lateral pterygoid muscle (LP). The mandible is in the early stage of development along the Meckel's cartilage (MC). The medial pterygoid muscle (MP) is located in the inferior side rather than medial side of the lateral muscle. Asterisk in panel B indicates an artefactual damage during the histological procedure. DP, digastricus muscle posterior belly; ECA, external carotid artery; IJV, internal jugular vein; M, masseter muscle; SCM, sternocleidomastoideus muscle; TG, trigeminal ganglion; VII, facial nerve; XI, accessory nerve. BN, buccal nerve; CP, coronoid process of the mandible; CTN, chorda tympani nerve; DTN, deep temporal nerves; IAN, inferior alveolar nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; LN, lingual nerve; LP, lateral pterygoid muscle; MC, Meckel's cartilage; MN, mandibular nerve; Mn, masseter nerve; MP, medial pterygoid muscle; MXA, maxillary artery; MXN, maxillary nerve; OG, otic ganglion; PT, cartilaginous pterygoid part of the sphenoid (independent of the other parts); PTT, pharyngotympanic tube; RC, Reichert's cartilage; SP, sphenoid bone anlagen; T, temporalis muscle; ZA, zygomatic arch.
