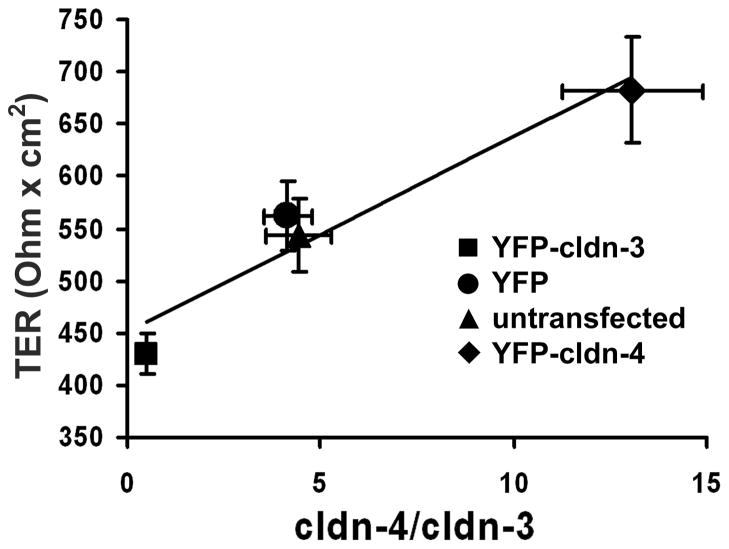
Figure 4. Differential effect of increasing cldn-3 or cldn-4 on alveolar epithelial cell barrier function.
Model type I alveolar epithelial cells transduced with YFP-cldn-3 (■), YFP-cldn-4 (◆), YFP-control virus (●) or untransfected controls (▲) were assessed for the effect of altering claudin expression on barrier function, as determined using transepithelial resistance (TER; Ohm × cm2) (y axis). The expression ratio cldn-4/cldn-3 was determined by immunoblot (x axis) demonstrating that there was a linear relationship between cldn-4/cldn-3 ratio and TER (r2 = 0.93). Cells expressing increased cldn-3 had significantly lower TER than either control cells or cells expressing increased cldn-4 (P < 0.05). Increasing cldn-4 also significantly increased barrier function (P < 0.05). Adapted from Mitchell, et. al. 40.