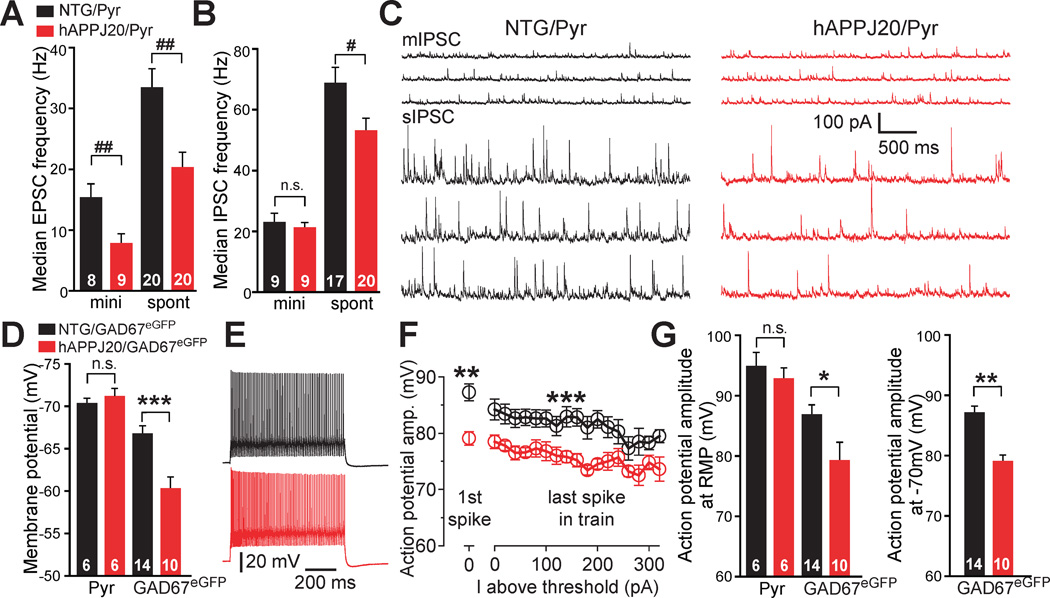
Figure 2. Inhibitory Synaptic Impairments and PV Cell Dysfunction in hAPPJ20 Mice.
(A–C) Synaptic alterations in layer II/III pyramidal neurons (Pyr) of the parietal cortex in hAPPJ20 (hAPPJ20/Pyr; red) and NTG (NTG/Pyr; black) mice. (A, B) Frequency of miniature (mini, m) and spontaneous (spont, s) excitatory (A) and inhibitory (B) postsynaptic currents (mIPSC, sIPSC, mEPSC, and sEPSC). #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney two-sample rank test). (C) Recordings of mIPSCs (upper panels) and sIPSCs (lower panels). (D–G) Synaptic alterations in fast-spiking GABAergic cells of the parietal cortex in GAD67eGFP transgenic mice without (NTG/GAD67eGFP; black) or with hAPP (hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP; red) expression. (D) Resting membrane potential (RMP) of pyramidal cells and fast-spiking GABAergic cells. ***p<0.001 (t test). (E) Spike traces from fast-spiking GABAergic cells (red) evoked by 800-ms current of 380 pA. (F) Mean action potential amplitudes for the first spike at threshold and for the last spike of the train at each 20-pA-current step above threshold. Neurons were held at −70 mV between current steps (n=10–14 cells per genotype). **p<0.01 (t test), ***p<0.001 (two-way ANOVA). (G) Reduced action potential amplitudes for the first spike at threshold in fast-spiking GABAergic cells of hAPPJ20/GAD67eGFP mice. Neurons were at RMP (left) or held at −70 mV (right) between current steps. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (t test). Numbers in bars are cells (A, B, D, G). Values are mean ± SEM. See Figure S2 and Table S1 for supporting data.