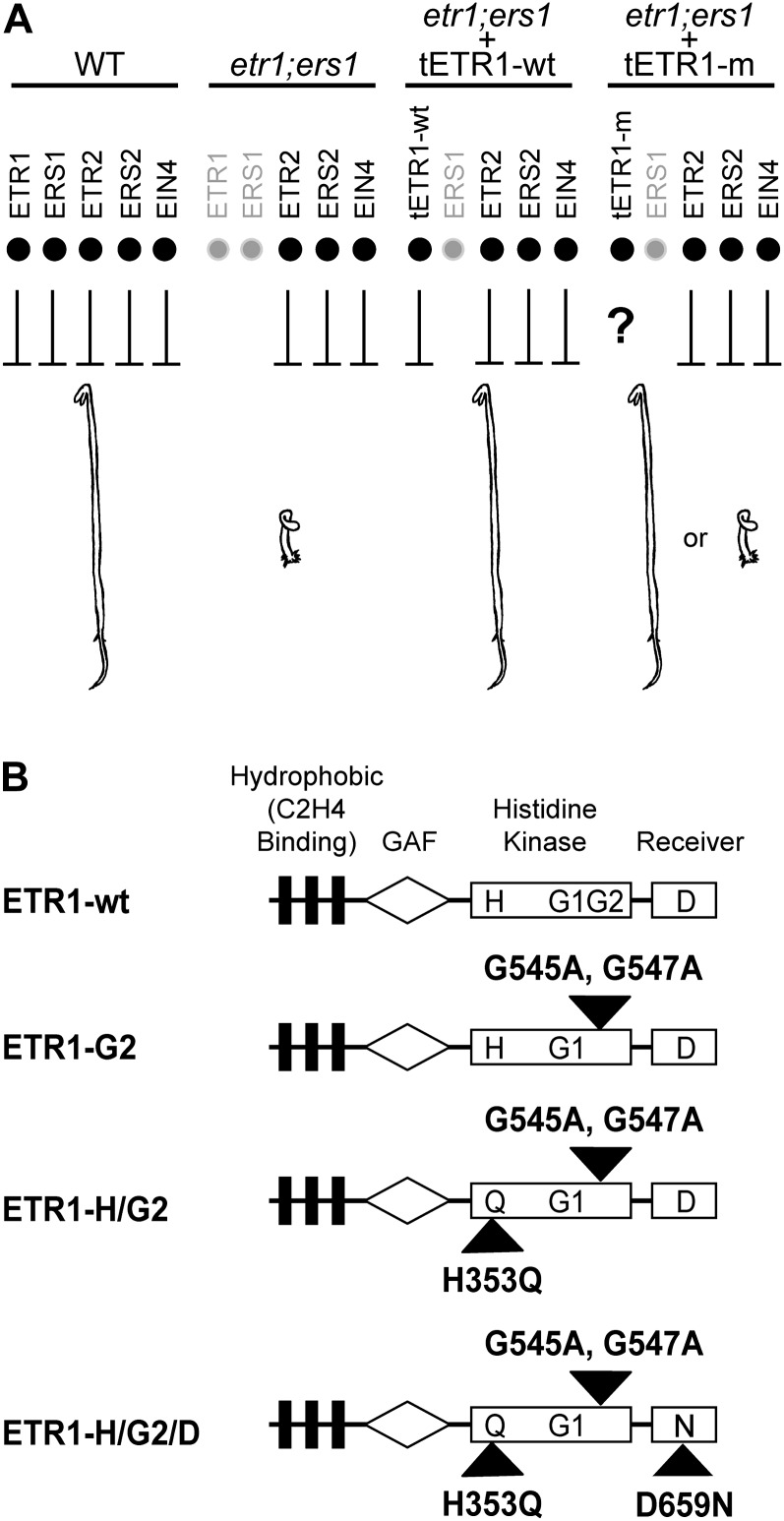
Figure 1.
Experimental strategy and constructs used for analysis. A, Effect of subfamily 1 receptors on the repression of ethylene responses. In wild-type (WT) plants, all five ethylene receptors serve to repress ethylene responses. In the etr1-9;ers1-3 double mutant (etr1;ers1), the remaining subfamily 2 receptors (ETR2, ERS2, and EIN4) are not sufficient to repress ethylene responses, and dark-grown seedlings show a constitutive ethylene-response phenotype. Transgenic expression of ETR1 (tETR1-wt) in the etr1-9;ers1-3 background rescues the mutant phenotype. Other modified versions of ETR1 (tETR1-m) can then be tested to determine if they rescue the mutant etr1-9;ers1-3 phenotype. B, Structure of ETR1 and constructs used for analysis. The hydrophobic ethylene-sensing domain, the GAF domain, the His kinase domain, and the receiver domain are indicated. The predicted phosphorylation sites are indicated by H for His-353 and D for Asp-659. G1 and G2 indicate the positions of the G1 and G2 boxes within the kinase domain. Black triangles indicate the positions of site-directed mutations introduced to eliminate His kinase activity.