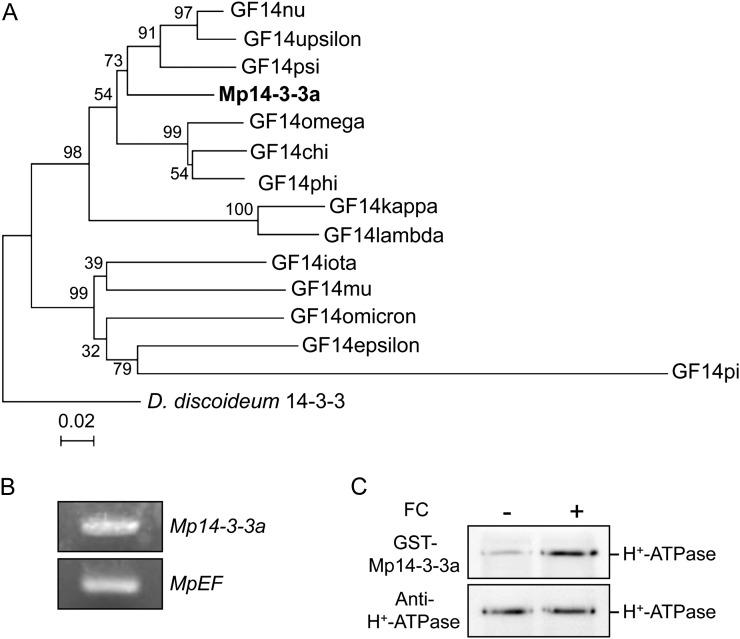
Figure 3.
Molecular characterization of 14-3-3 protein in M. polymorpha. A, Phylogenetic tree of 14-3-3 proteins from M. polymorpha (Mp14-3-3a), Arabidopsis (GF14chi, GF14omega, GF14psi, GF14phi, GF14upsilon, GF14lambda, GF14nu, GF14kappa, GF14mu, GF14epsilon, GF14omicron, GF14iota, GF14pi), and Dictyostelium discoideum 14-3-3 (X95568). The alignment for the phylogenetic tree was performed with ClustalW using full-length amino acid sequences (Thompson et al., 1994). The phylogenetic tree was created with the MEGA5 software (Tamura et al., 2011) and the neighbor-joining program with 1,000 bootstrap replications. Bootstrap values at the branches represent the percentage obtained in 1,000 replications. The D. discoideum 14-3-3 sequence was used as an outgroup. The scale bar represents 0.02 substitutions per site. B, RT-PCR analysis of 14-3-3 protein expression in M. polymorpha thalli. Total RNA was extracted from thalli, and RT-PCR was performed. MpEF was used as a loading control. C, FC-induced binding of 14-3-3 protein of M. polymorpha to the phosphorylated H+-ATPase. Procedures were the same as in Figure 2. Binding of 14-3-3 protein was detected by protein blot using GST-Mp14-3-3a as probe.