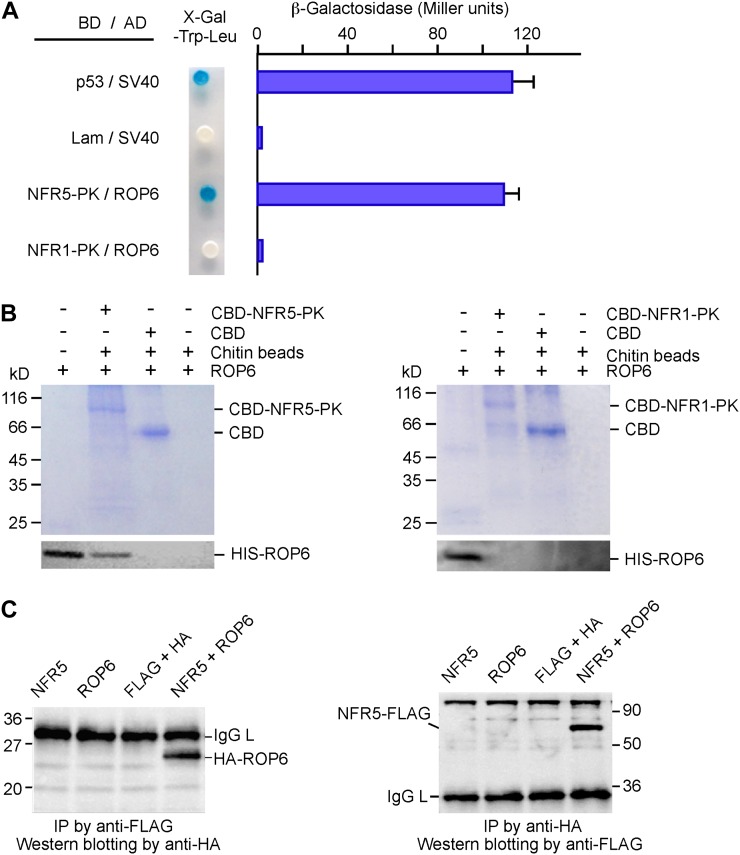
Figure 2.
Interaction between ROP6 and NFR5. A, Yeast two-hybrid assays. ROP6 was expressed as a fusion protein with the activation domain (AD in pGADT7); NFR1-PK and NFR5-PK were expressed as fusion proteins with the Gal4 DNA-binding domain (BD in pGBKT7). Yeast cells harboring the plasmids were grown on SD/-Leu-Trp medium containing X-gal (left). The strength of the interaction was evaluated by β-galactosidase activity (right). The combinations p53/SV40 and Lam/SV40 served as positive and negative controls, respectively. NFR1-PK was used to replace NFR5-PK for testing interaction specificity. B, In vitro protein pull-down assay. Purified soluble ROP6 was mixed with CBD-tagged NFR5-PK (left), which was immobilized to chitin beads. After washing, proteins pulled down by chitin beads were separated on SDS-PAGE gels. The gels were stained with Coomassie blue (top) or used for western blotting using anti-ROP6 antibodies (bottom). As a control for interaction specificity, CBD-tagged NFR1-PK was used to replace CBD-tagged NFR5-PK in the same assay (right). The positions of CBD and CBD-tagged NFR-PK are indicated. C, Coimmunoprecipitation of proteins expressed in plants. FLAG-tagged NFR5 and HA-tagged ROP6 were expressed in leaves of tobacco via Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation. A leaf extract or a mixture of two extracts was incubated with anti-FLAG antibody, followed by reaction with protein G beads. Immunoprecipitates (IP) were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody (left). The same experiment was performed again except that the order of antibody uses was reversed. Anti-HA antibody was used to precipitate the immunocomplex, and anti-FLAG antibody served as the primary antibody in western-blot analysis (right). Molecular masses of marker proteins in kD and the positions of ROP6, NFR5, and IgG light chain (IgG L) are indicated. [See online article for color version of this figure.]