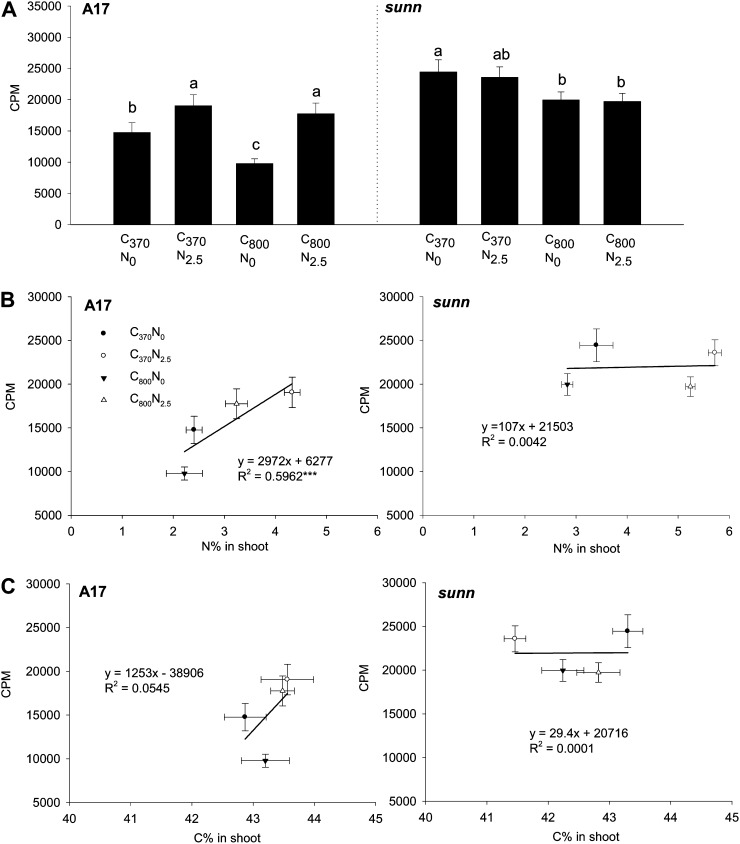
Figure 4.
Shoot-to-root auxin transport phenotypes in response to C and N treatments. A, Total transported [3H]IAA (in cpm) in 10-d-old, mock-inoculated cv Jemalong A17 and sunn-1 seedlings grown in ambient C (370 μL L−1 CO2 [C370]), high C (800 μL L−1 CO2 [C800]), minus N (0 mm nitrate [N0]), and/or plus N (2.5 mm nitrate [N2.5]). Radiolabeled auxin was applied between the cotyledons at the shoot apex and allowed to transport into the root. After 3 h, eight 5-mm segments, starting just below the cotyledons, were excised into scintillation fluid. Segment 1 was not taken into account for the analysis because of diffusion from the site of application. The results show the sum of the total amount of radiolabeled auxin transported into segments 2 to 8 as means ± se (n = 16–20). Treatments labeled with different letters differ significantly within one genotype (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA). B, Correlation of total shoot-to-root auxin transport with N concentration in the shoot. C, Correlation of total shoot-to-root auxin transport with C concentration in the shoot. Significant correlations are marked with asterisks (*** P < 0.001 [calculated with unbalanced linear regression]).