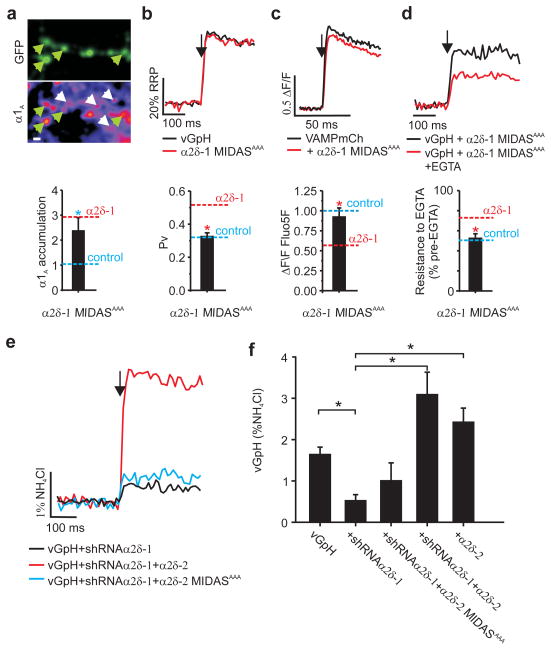
Figure 4. α2δ MIDAS motif is essential for coupling Ca2+ channels to exocytosis.
a,Top: Presynaptic α1A abundance. Green arrows indicate transfected boutons, white arrows indicate non-transfected immunopositive α1A channel puncta.. Scale bar = 2 μm. Bottom: Ratio of α1A staining in synaptic boutons. Dashed lines represent ratios taken from Fig. 1f as indicated. b, Top: Representative vGpH responses to 1 AP (arrow) as a fraction of the measured RRP Bottom: vGpH and α2δ-1 MIDASAAA (Pv=0.33±0.017) compared to data from Fig. 2f as indicated. c, Top: Representative responses to 1 AP-driven Ca2+ influx (Fluo5F 3F/F). Bottom: Peak 1 AP Fluo 5F ΔF/F values in cells co-transfected with VAMPmCh (n=11) and α2δ-1 MIDASAAA (0.88±0.1; n=6) normalized to VAMPmCh alone (*p<0.05). d,Top: Representative vGpH response to 1 AP in a neuron co-expressing α2δ-1 MIDASAAA as indicated. Bottom: Resistance to EGTA block (% block = 51±5, p=0.63) dashed lines compare data from Fig. 3e as indicated. e, Representative vGpH responses to 1 AP. f, 1 AP response (%NH4Cl): vGpH=1.65±0.17; vGpH+α2δ-1shRNA=0.4±0.08, v G p H +α2δ-1shRNA+α2δ-2=3.10±.53; vGpH+α2δ-1shRNA+α2δ-2 MIDASAAA=1.02±.41; vGpH+α2δ-2=2.44±0.36. Values are mean±SEM, *p<0.01, n≥7, (*p<0.05).