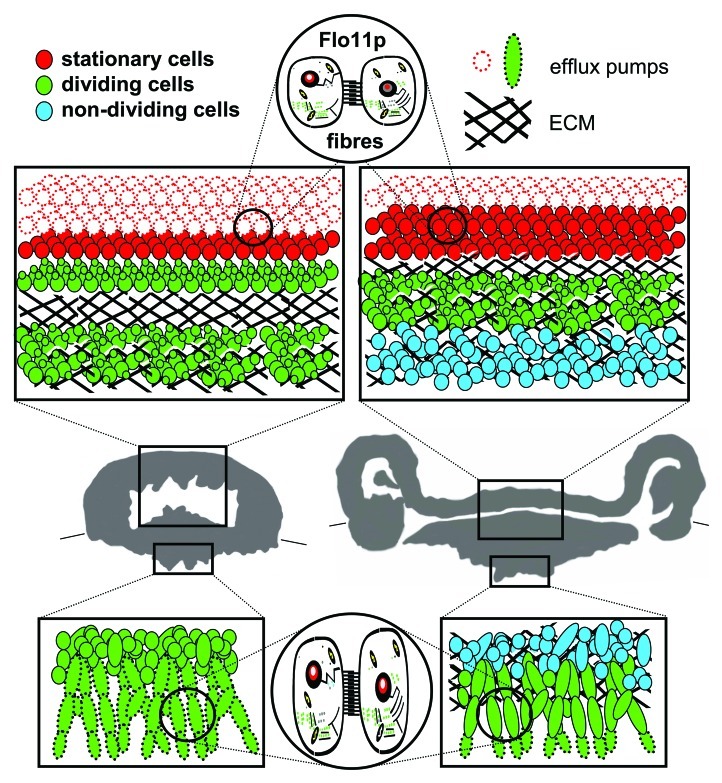
Figure 1. Internal structure of colony of feral Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. Thirty-six h-old (left) and 72 h-old (right) colony. Boxes in vertical colony cross-sections summarize structure and function of cell subpopulations in upper aerial and bottom subsurface colony parts; the localization of dividing, non-dividing and stationary cells is depicted, as well as cells with active drug efflux pumps Pdr5p and Snq2p. The presence of ECM is marked with black line hatching. Flo11p-dependent fibers interconnect cells in both aerial and subsurface colony parts.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.