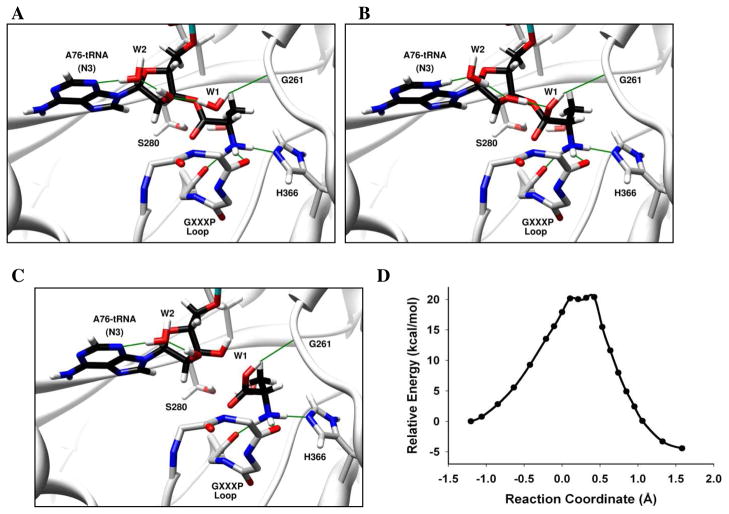
Figure 2. Deacylation of Ala-tRNAPro by E. faecalis ProRS INS domain via A76 as general base.
(A) Catalytic water (W1) is activated by the 2′-OH. (B) A proton transfer occurs from W1 to N3 of A76 via the 2′-OH and W2 to form a protonated A76 intermediate. (C) A proton is subsequently transferred to O3′ via W2 and 2′-OH to form the hydrolyzed product. The oxyanionic intermediate is stabilized by the GXXXP loop. The reaction coordinate refers to bond broken (Ala-C(O) – O3′-A76) – bond formed (Ala-C(O) – OH2). Panels A, B and C show the optimized reactant, intermediate, and products, respectively. (D) The calculated potential energy surface for this mechanism at the BP86/TZVPP//BP86/SV(P) level of theory for the QM domain.