Figure 3.
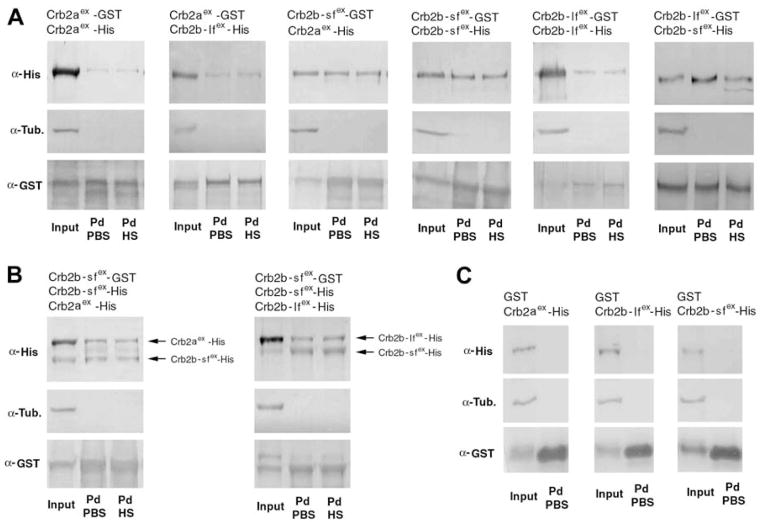
The extracellular domains of Crb2a, Crb2b-lf, and Crb2b-sf mediate homophilic and heterophilic physical adhesion. Various combinations (indicated above the blots) of GST and His fusions of the extracellular domains of Crb2a, Crb2b-lf, and Crb2b-sf were co-expressed in sf9 cells. The cell lysates were analyzed by GST pulldown and Western blotting assays. Anti-GST blots confirmed the efficient pulldown of GST fusion proteins. Anti-α-tubulin blotting indicated the absence of cytoplasmic protein contamination in the pulldown fractions (Pd). The pulldown fractions were washed either with PBS (PBS) only or with PBS as well as 1M NaCl high salt solution (HS). A. Pulldown analyses of pair-wisely co-expressed GST- and His-fusions indicated that the extracellular domain of Crb2a, Crb2b-lf, and Crb2b-sf physically adhered to each other both homophilically and heterophilically. In addition, the adhesion was strong enough to withstand high ionic washes. B. Competition pulldown analyses revealed that Crb2b-sfex-GST bound to Crb2b-sfex-His more efficiently than it bound to Crb2b-lfex-His or Crb2aex-His, as suggested by the higher ratios between Crb2b-sfex-His and its Crb2b-lfex-His or Crb2aex-His competitors in the pulldown fractions than in the input fractions. C. As specificity controls, when co-expressed with Crb2aex-His, Crb2b-lfex-His, or Crb2b-sfex-His, GST itself did not pull-down any Crb-His fusions, indicating that these His-fusions did not bind to GST or glutathione resin non-specifically.