Figure 3.
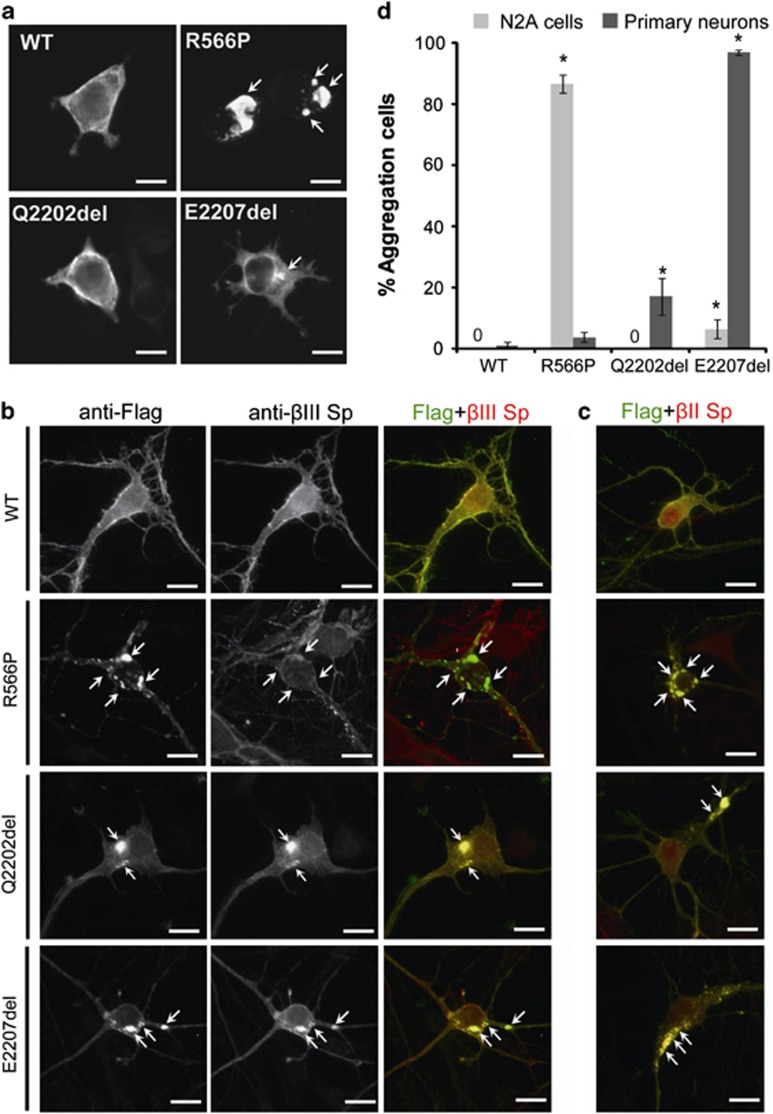
Mutant α-II spectrin cause aggregation of α/β spectrin heterodimers. (a) The wildtype (WT) and the three mutant α-II spectrins were detected by immunofluorescence in transfected N2A cells. The WT α-II spectrin and p.Q2202del mutant were similarly expressed at cell periphery. However, the p.R566P and p.E2207del α-II spectrin mutants showed large and small aggregations (arrows), respectively. (b, c) Expression of the WT and the three mutant α-II spectrins at 7 days in vitro in primary cortical neurons. Flag tagged WT α-II spectrin was expressed at cell extensions and periphery, overlapping with the expression of β-II and β-III spectrins. Three mutant α-II spectrins (R566P, Q2202del, and E2207del) showed aggregation in cell bodies and neurites (arrows). Aggregations caused by the Q2202del and E2207del mutants were colocalized with both β-II and β-III spectrins (lower two panels). Aggregations caused by the R566P mutant were colocalized with β-II spectrin, but their colocalization with β-III spectrin was not evident. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (d) N2A cells and primary cortical neurons showing α-II spectrin aggregation were counted: Numbers of aggregated/total numbers of counted cells (expressing transfected α-II spectrin) in three experiments: N2A, WT: 0/194, R566P: 212/244, Q2202del: 0/241, E2207del: 9/180; primary neurons, WT: 3/300, R566P: 11/300, Q2202del: 51/300, E2207del: 291/300. Asterisks indicate that a significant difference (P<0.01) was observed compared with WT by Bonferroni's posttest analysis. The scale bar represents 10 μm.