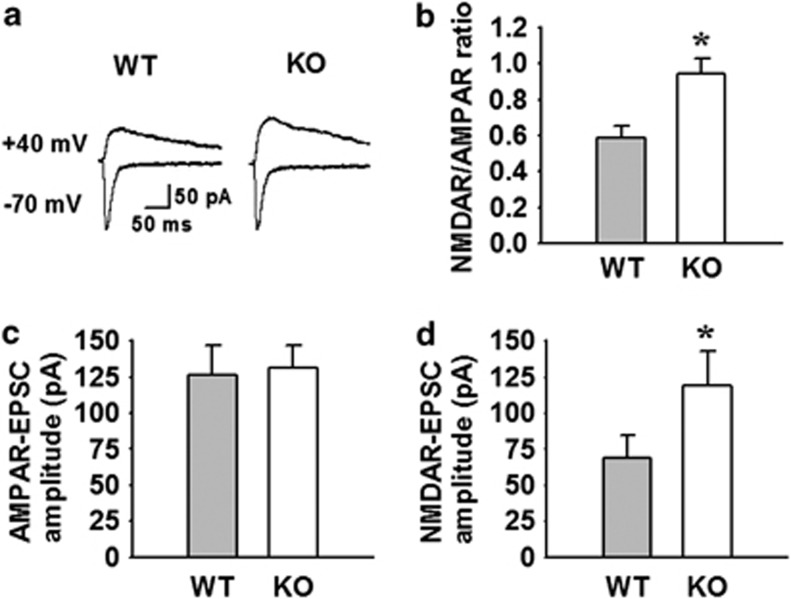
Figure 4.
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) deficiency selectively increases N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR)-mediated currents in the lateral amygdala (LA). (a) Representative traces of AMPA receptor (AMPAR) (lower traces)- and NMDAR (upper traces)-mediated excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in AQP4 wild-type (WT) and knockout (KO) mice. Stimulus artifacts were omitted for clarity. (b) Summary histogram for the ratio of NMDAR- to AMPAR-mediated EPSC amplitudes in WT and KO mice. The NMDAR/AMPAR ratio was significantly larger in KO mice (0.95±0.09, n=4 cells from 4 mice) than in WT mice (0.59±0.06, n=4 cells from 4 mice), *P<0.05 vs WT. (c) Summary histograms for AMPAR-mediated EPSCs in WT and KO mice. The mean amplitudes of AMPAR-mediated EPSCs were not significantly different among groups. (d) Summary histograms for NMDAR-mediated EPSCs in WT and KO mice. The mean amplitudes of NMDAR-mediated EPSCs of KO mice (119.1±23.4 pA) were significantly increased compared with those in WT mice (68.5±16.0 pA). *P<0.05 vs WT.