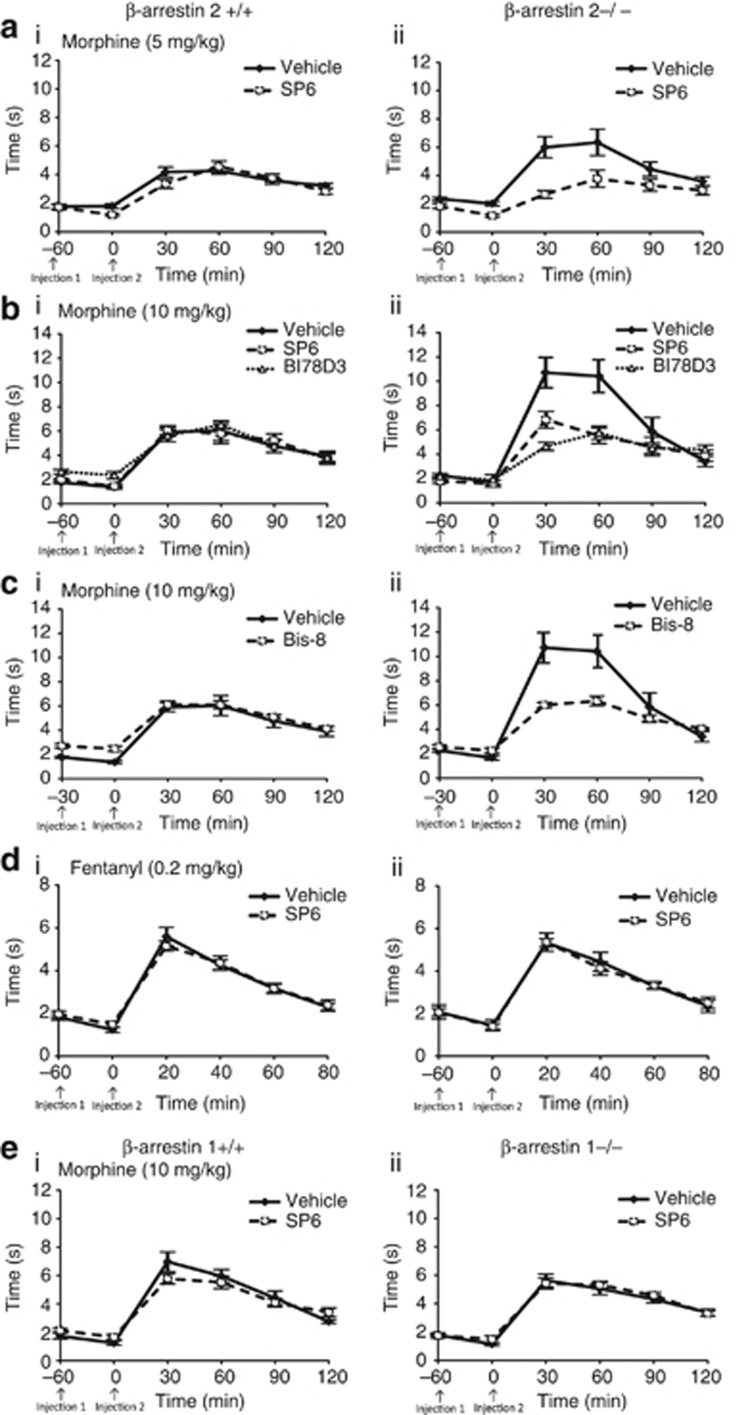
Figure 2.
The enhanced thermal analgesic effect of morphine in β-arr2−/− mice is reduced to +/+ levels by inhibiting JNK or PKC. The warm-water (49.5 °C) tail-immersion assay was used to assess the analgesic effects of different mu agonists in β-Arr2+/+ and −/− mice and the resultant data are presented as the response (s; y axis) over time (min; x axis). (a, b) β-Arr2−/− mice showed a dose-dependent increase in the thermal analgesic effects of morphine ((a) 5 and (b) 10 mg/kg morphine s.c., 5 mg/kg: p=0.12 vs β-arr2+/+, F1,5=1.773; 10 mg/kg: p<0.001 vs β-arr2+/+, F1,5 13.227), which was reversed by the JNK inhibitor, SP6 (aii) 5 mg/kg: p<0.05 vs vehicle, F1,5=2.422; (bii) 10 mg/kg: p<0.01 vs vehicle, F1,5=4.501). BI78D3 (bii), similarly reversed the enhanced analgesia seen in morphine-treated (10 mg/kg s.c.) β-arr2−/− mice (p<0.001 vs vehicle, F1,5=6.142). Neither JNK inhibitor altered the β-arr2+/+ response ((ai) 5 mg/kg: p=0.06 vs vehicle, F1,5=10.74; (aii) 10 mg/kg: SP6: p=0.94 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.457; BI78D3: p=0.71 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.575) (c) The PKC inhibitor Bisindolylmaleimide VIII (10 mg/kg i.p.) also reversed the enhanced analgesia seen after morphine administration (10 mg/kg s.c.) in β-arr2−/− mice (p<0.001 vs vehicle, F1,5=7.099), while having no effect in β-arr2+/plus; mice (p=0.76 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.937). (d) Mice treated with fentanyl (0.2 mg/kg s.c.) showed no effect of the β-arrestin 2 deletion (p=0.84 vs β-arr2+/+, F1,5=0.403) or JNK inhibition (β-arr2+/+: p=0.59 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.748; β-arr2−/−: p=0.96 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.194). (e) There was also no effect of deleting β-arrestin 1 (p=0.10 vs β-arr2+/+, F1,5=1.883) or JNK inhibition on the morphine response of β-arr1−/− or +/+ mice (SP6: β-arr1+/+: p=0.07 vs vehicle, F1,5=2.089; β-arr1−/−: p=0.80 vs vehicle, F1,5=0.224). Injection 1=JNK or PKC inhibitor, or matching vehicle. Injection 2=morphine or fentanyl.