Figure 2.
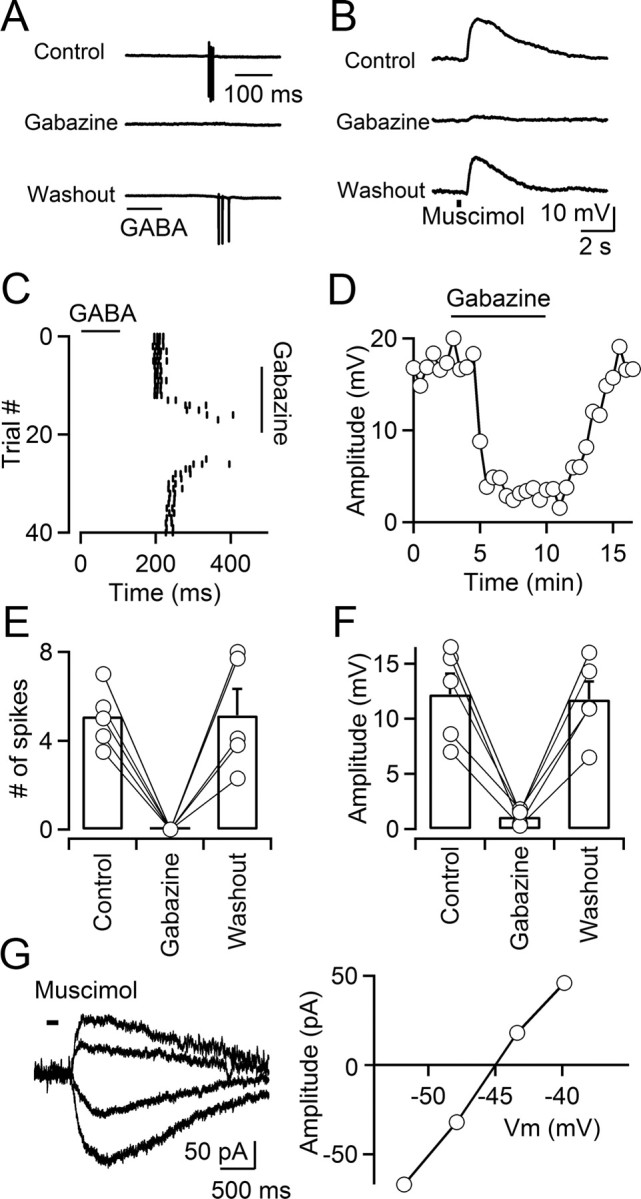
Activation of GABAA receptors depolarizes TRN neurons. A, C, E, GABA induces action potentials in TRN neurons. A, A representative experiment showing that brief puffs of GABA (300 μm; 100 ms; time of application indicated by the bar) elicits action potentials in a TRN neuron in the presence of a GABAB antagonist, recorded in cell-attached voltage clamp. Action potential firing is reversibly blocked by bath application of the GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine (10 μm). C, Raster plot shows timing of GABA-evoked action potential firing over multiple trials during wash-in and washout of gabazine, for the neuron shown in A. E, Summary data showing that GABA-induced action potentials were reversibly blocked by gabazine (n = 5; p < 0.001, paired Student's t test). Error bars indicate SEM. B, D, F, Activation of GABAA receptors elicits postsynaptic depolarizations. B, For a neuron recorded in cell-attached current-clamp mode, brief application of the GABAA receptor agonist muscimol (500 μm; 300 ms; time of application indicated by the bar) evoked postsynaptic depolarizations that were reversibly blocked by gabazine (10 μm). Recordings were performed in the presence of TTX (0.5 μm). D, Plot showing the time course of the muscimol-induced response amplitude during wash-in and washout of gabazine, for the neuron shown in B. F, Summary data showing that muscimol-induced responses were reversibly blocked by gabazine (n = 5; p < 0.001, paired Student's t test). G, Left, Muscimol-induced membrane currents evoked at different command potentials (−63 to −38 mV) measured with gramicidin D perforated-patch recordings. Application of muscimol (100 μm; 200 ms duration) is indicated by the bar. Right, The graph plots the current–voltage relationship of the muscimol-evoked response. Currents were evoked in the presence of TTX (0.5 μm).
