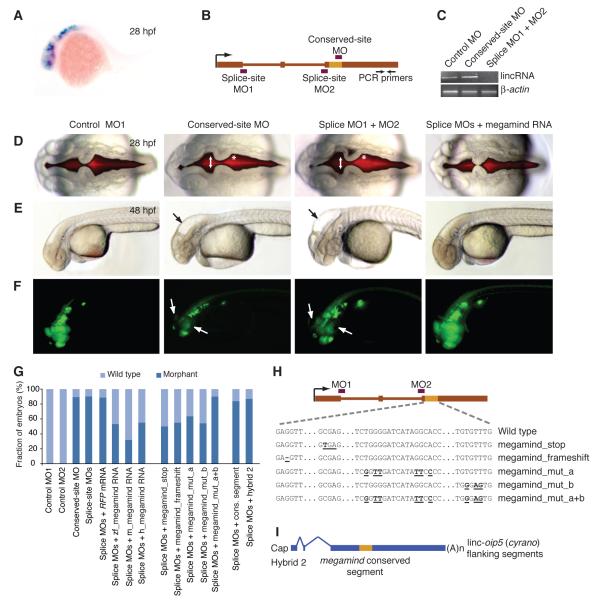
Figure 6. The Importance of linc-birc6 (megamind) for Proper Brain Development.
(A) In situ hybridization showing megamind expression in the brain and eyes of zebrafish embryos at 28 hpf.
(B) Gene architecture of megamind, showing the hybridization sites of the MOs (red boxes) and RT-PCR primers (arrows).
(C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of mature megamind in embryos at 72 hpf that had been injected with the indicated MOs. β-actin mRNA was used as a control.
(D) Brain ventricles after injection with either the indicated MOs or co-injected with the splice-site MO and mature mouse megamind RNA, visualized using a red fluorescent dye injected into the ventricle space at 28 hpf. An expanded midbrain ventricle (arrow) and abnormal hindbrain hinge point (asterisk) are indicated.
(E) Embryos at 48 hpf that had been injected with the indicated reagents. Abnormal head shape and enlarged brain ventricles are indicated (arrow).
(F) Embryos at 48 hpf that had been injected with the indicated reagents. NeuroD-positive neurons in the retina and nasal placode were marked with GFP expressed from the neurod promoter (Obholzer et al., 2008). Near absence of NeuroD-positive neurons in the retina and tectum (arrows) is indicated.
(G) Frequency of morphant phenotypes in injected embryos (Table S5).
(H) Schematic of DNA point substitutions in the megamind conserved segment.
(I) Architecture of a hybrid transcript containing the megamind conserved segment in the context of cyrano flanking sequences.