Figure 1. Impact of p63-SAM mutations on palate development.
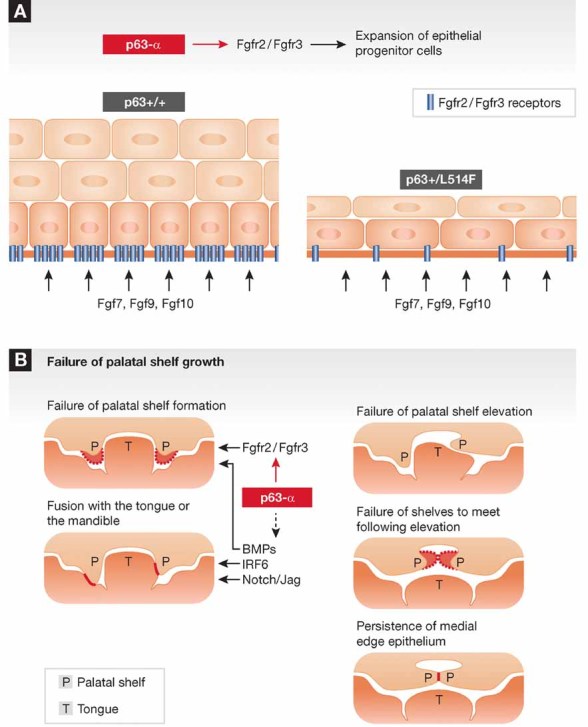
- ΔNp63α functions as a positive determinant of FGFR2 and FGFR3 expression. Mutations found in AEC syndrome are sufficient to suppress, in a heterozygous state, FGFR2 and FGFR3 expression. This causes an impairment of proliferation in embryonic ectodermal cells.
- p63 is interconnected with several pathways that are required for one or more steps of secondary palate development as recently reviewed (Dixon et al, 2011).
